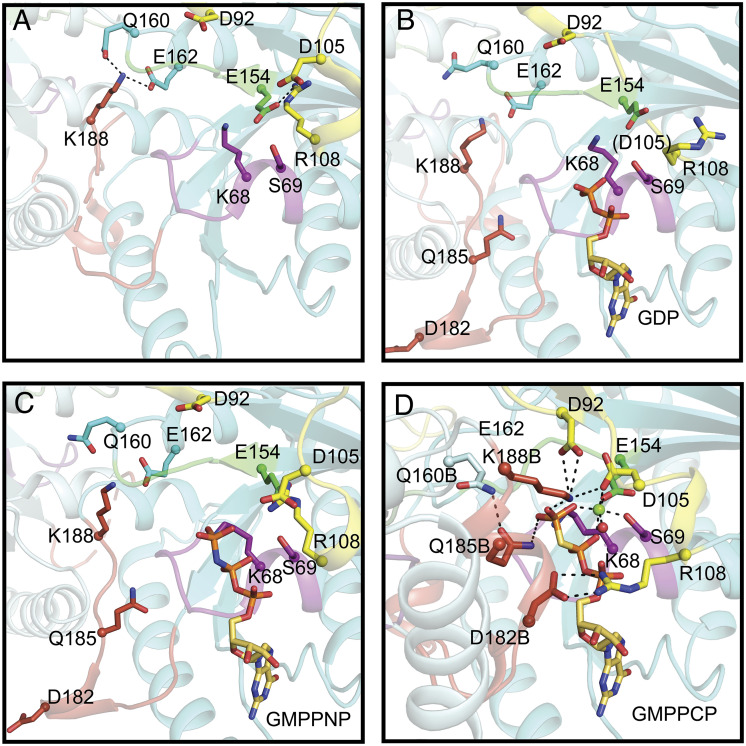
Fig. 4.
Comparison of the interactions of nucleotide-binding sites in MeaB structures with MeaB:MeMCMcbl:GMPPCP structure. (A) Nucleotide-free MeaB (PDB 2QM8). P-loop (purple), switch I (yellow), switch II (green), switch III (red orange), additional residues that are outside of the motifs that undergo conformational rearrangements (cyan). Base specificity loop interactions are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S4 instead of here for clarity. (B) GDP-bound MeaB (PDB 2QM7). (C) GMPPNP-bound MeaB (PDB 4JYB). (D) GMPPCP-bound MeaB in the presence of MeMCMcbl (this work). The residues shown in sticks undergo nucleotide-dependent interactions that contribute to the conformational changes necessary to increase GTP hydrolysis and communicate with the mutase. Lys188B and Gln185B are ~2.1 Å and ~3.5 Å from the γ-phosphate of GMPPCP, respectively. Lys188B is also ~3.4 Å away from Asp92. The “B” label indicates residues from MeaB chain B.