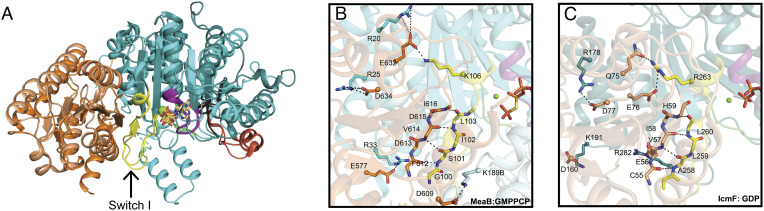
Fig. 5.
Interactions at the interface of the MeaB and MeMCMcbl in the MeaB:MeMCMcbl:GMPPCP complex. (A) Superimposition of MeMCMcbl (orange) and one protomer of MeaB (cyan) from the MeaB:MeMCMcbl:GMPPCP complex on the Cbl-binding domain (light orange) and G-protein domain (teal) from IcmF (PDB 4XC6) shows a similar interface between domains. Additionally, the conserved regions of the G-protein are in similar orientations. Coloring: Base loop (dark brown), P-loop (purple), switch I (yellow and labeled with an arrow), switch II (green), and switch III (red orange). (B) The interface between MeaB (cyan with switch I region in yellow) and MeMCMcbl (orange) primarily consists of the hydrogen bonding of two β-strands, one from MeaB (switch I residues 100 to 103 in yellow) and one from MeMCMcbl (residues 612 to 616 in orange). The side chains of the β-strands are omitted for simplicity. Additionally, the interface has five observed salt bridges, K189B:D609, K106:D632, R33:E577, R25:D634, and R20:D632. The “B” indicates residues from MeaB chain B. (C) The interface between the G-protein domain (teal with switch I in yellow) and the Cbl-binding domain (light yellow) of IcmF (PDB 4XC6) primarily consists of hydrogen bonding to two β-strands, one from the G-protein domain (switch I residues 258 to 260 in yellow) and one from the Cbl-binding domain (residues 55 to 59 also yellow), shown as sticks. The side chains of the β-strands are omitted for simplicity. Additionally, the interface has five observed salt bridges, R178:D77, K191:D160, R263:Q75, R263:E76, and R282:E56.