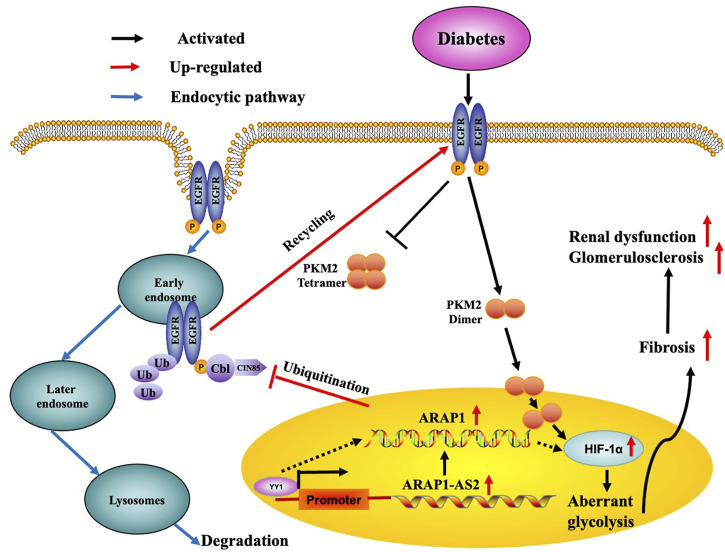
FIGURE 10.
Schematic representation of the proposed model: possible regulatory mechanism of YY1, ARAP1-AS2, and ARAP1 on HIF-1α accumulation and aberrant glycolysis in DKD. Increased YY1 expression in a high-glucose environment can upregulate ARAP1-AS2 expression by targeting its promoter and then indirectly upregulate ARAP1 expression. Subsequently, ARAP1 binds to CIN85 and reduces the ubiquitination of EGFR, thus stabilizing total EGFR protein levels to support the persistent activation of EGFR in DKD. The persistent activation of EGFR then promotes PKM2 dimer expression and nucleus translocation to activate HIF-1α, accompanied by reducing tetramer formation, which finally leads to aberrant glycolysis and aggravates ECM accumulation and glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis in human glomerular mesangial cells exposed to high glucose and diabetic db/db mice.