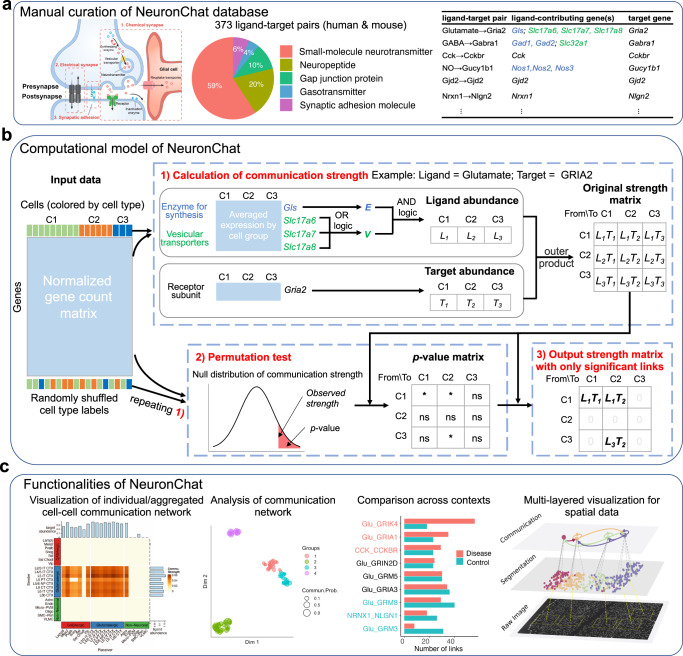
Fig. 1. Overview of NeuronChat.
a Overview of NeuronChat database. NeuronChat database includes ligand-target pairs required for chemical synapse, electrical synapse and synaptic adhesion (left panel). There are a total of 373 ligand-target pairs for both human and mouse, curated into five categories based on the type of the ligand (middle panel). The interaction pair list includes the ligand, target, and genes contributing to them (right panel). Note that genes contributing to the ligand are categorized into different groups (indicated by colors) based on their biological functions such as synthesis or vesicular transport. b Schematic diagram to illustrate the computational model of NeuronChat. The communication strength characterizes the coordinated expression of genes required for ligand emission in the sender cell group, and the expression of the target gene in the receiver cell group. The statistical significance of a communication link is determined by the permutation test (* and ns represent significant and not significant, respectively). Only significant links are kept in the output communication strength matrix while values for not significant links are set to be zeros. See Methods for details. c Functionalities of NeuronChat: visualization and analysis of the intercellular communication networks, making systemic comparisons across different biological contexts, and multi-layered visualization for spatial transcriptomics.