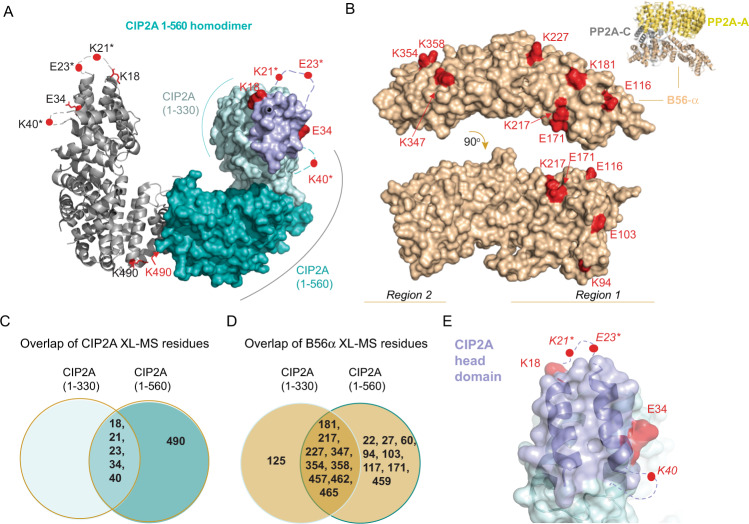
Fig. 1. CIP2A interacts with B56α via its N-terminal head domain.
A In red are indicated CIP2A(1-560) residues identified in inter-molecular cross-links to B56α using DSS and DMTMM cross-linkers. CIP2A 1-560 homodimer (PDB: 5UFL) monomers are shown either as ribbon or space filling models. In the space filling model 1-330 amino acids are in cyan including in purple the CIP2A head domain identified in this study. The 331-560 region including the dimerization domain is shown as turquoise. Due to high molecular flexibility of the N-terminal region of CIP2A, positions of residues K21 and E23 (indicated with*) had to be approximated using A24 position and K40 using position of R43. B Distribution of B56α (PDB: 6NTS) residues cross-linked to CIP2A by using DSS and DMTMM chemistries. Cross-linked amino acids are in red and roughly distributed to two distinct regions on B56α shown in two different B56α orientations. Insert shows the overall structural organization of PP2A-B56α trimer consisting of PP2A-A, PP2Ac, and B56α. C Overlap of the B56α cross-links identified for two different CIP2A fragments, 1-330 and 1-560. D Overlap of the CIP2A cross-links on B56α using CIP2A fragments, 1-330 and 1-560. D, E The indicated cross-link sites are combined from both the DSS and DMTMM experiments. E Zoom-into the CIP2A´s head domain, shown for one CIP2A monomer. CIP2A sites found in cross-links, with DSS and DMTMM, to B56α are in red, and the head domain (1-43 aa) is coloured in purple. Residue annotation is the same as in panel (A).