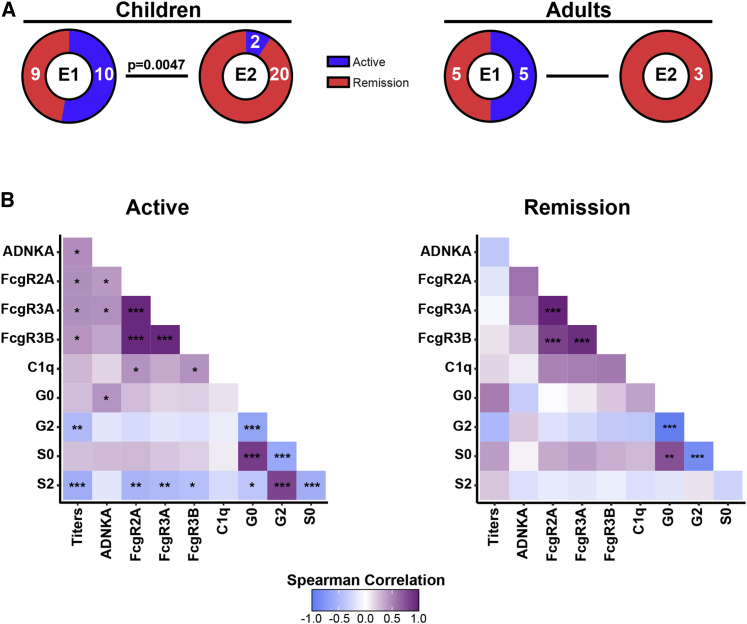
Figure 3.
E1 is characterized by active disease in MOGAD patients
(A) Frequency of active disease versus remission in E1 and E2 in children and adults. Fisher’s exact test was used for proportion comparisons in each age group (children p = 0.0047 and adults p = 0.2308). Numbers of individuals with active disease versus remission are indicated in each sector.
(B) Correlation matrix across MOG-specific ADNKA, titers, C1q, and activating FcgR (FcgR 2A, 3A, 3B) binding capacity, and Fc glycosylation profiles (G, galactosylation; S, sialylation) during active disease (left) or remission (right). Correlation strength is proportional to color intensity (r from −1 = negative correlation, blue, to +1 = positive correlation, purple). Features that were not significantly correlated in either group (age, B = bisecting GlcNAC, ADCD, inhibitory FcgR2B) are not reported (z scored, Spearman r correlation, Benjamini-Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons; ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001).