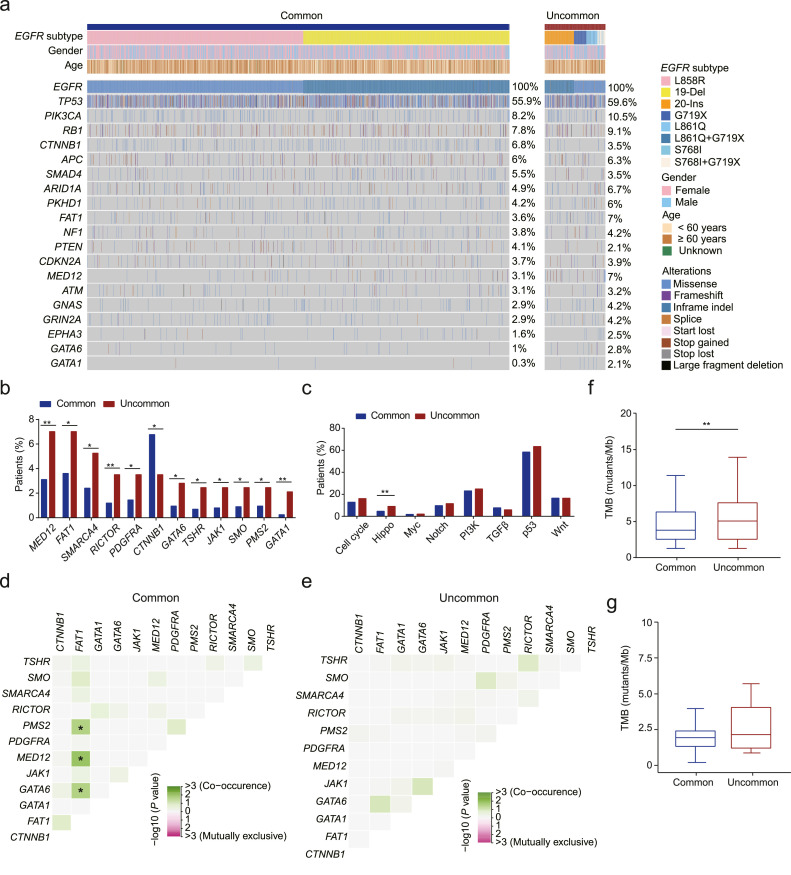
Fig. 1.
Somatic alterations associated with common and uncommon EGFR mutations. a. The genomic landscape of patients with common or uncommon EGFR mutations. Individual gene mutations in baseline tumor samples of EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients (N = 2280) were assessed by targeted NGS. Each column represents one patient. Clinical characteristics of patients are shown at the top. The frequency of each gene alteration is listed on the right. b. The bar plot shows the different distribution of somatic mutations in the cEGFR and uEGFR patient cohorts. c. The correlation between signaling pathways in which the concurrent mutations occur and EGFR subtypes. d-e. The heatmap demonstrates how frequently two somatic mutations occur in patients with cEGFR (d) or uEGFR mutations (e). f-g. Higher TMB was more likely associated with patients harboring uEGFR mutations than those carrying cEGFR mutations assessed by using the discovery study cohort (f) or the external validation cohort (g).