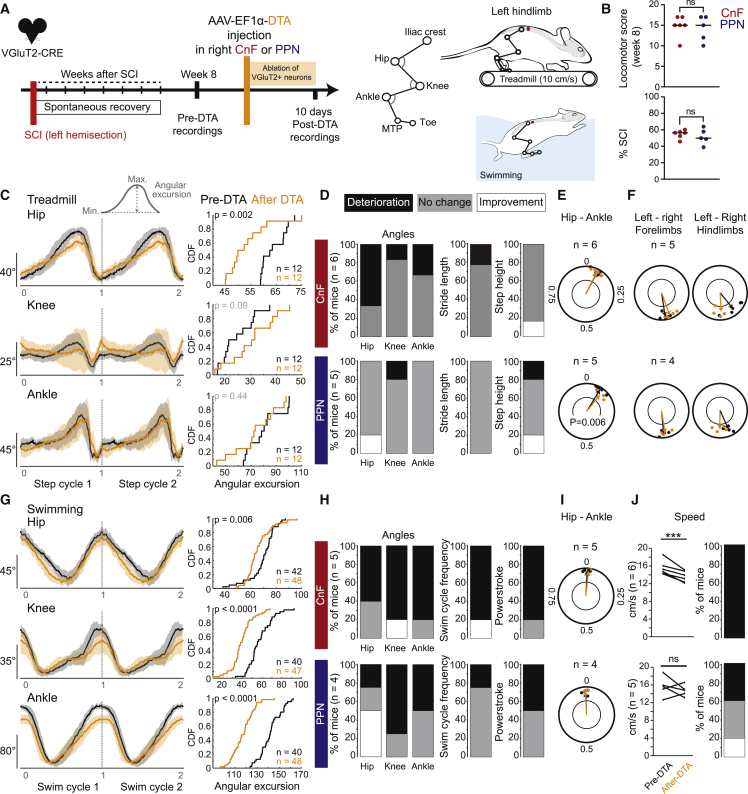
Figure 3.
Genetic ablation of contralesional glutamatergic CnF or PPN neurons impairs spontaneous locomotor recovery after chronic SCI
(A) Kinematic analysis before and after genetic ablation of glutamatergic neurons of the contralesional right CnF or PPN in chronic SCI mice.
(B) Locomotor score and extent of the SCI in both experimental groups (n = 6 CnF and n = 5 PPN, unpaired t test, p = 0.53 for the locomotor score; Mann-Whitney test, p > 0.9999 for the extent of SCI).
(C) Example from one mouse of the mean and SD of hip, knee, and ankle joint angles of the ipsilesional hindlimb during treadmill locomotion before and after genetic ablation of glutamatergic CnF neurons. Cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the angular excursion of hindlimb joints (n = step cycles, Mann-Whitney test or unpaired t test according to the normality of the distribution).
(D) Percentage of mice with significant decrease (detoriation), increase (improvement), or absence of change in the angular excursion of the joints, stride length, and step height. (Each mouse was compared with its pre-DTA level using a Mann-Whitney test or unpaired t test according to the normality of the distribution).
(E) Coupling between the angle of the ipsilesional hip and ankle (each circle represents a mouse, strength of the coupling for the PPN group, paired t test, p = 0.006).
(F) Bilateral fore- and hindlimb coupling for all mice (each circle represents a mouse, anchored on the right forelimb and hindlimb, respectively).
(G) Example from one mouse of the mean and SD of hip, knee, and ankle joint angles of the ipsilesional hindlimb during swimming before and after genetic ablation of glutamatergic CnF neurons. CDF of the angular excursion of hindlimb joints (n = swim cycles, Mann-Whitney test or unpaired t test according to the normality of the distribution).
(H) Percentage of mice with significant decrease (detoriation), increase (improvement), or absence of change in the angular excursion, swim cycle frequency, and power stroke (each mouse was compared with its pre-DTA level using a Mann-Whitney test or unpaired t test according to the normality of the distribution).
(I) Coupling between the angle of the ipsilesional hip and ankle for all mice (each circle represents a mouse).
(J) Average speed of each mouse before and after genetic ablation (paired t tests, p = 0.0006 for the CnF group and p = 0.77 for the PPN group) and percentage of mice with significant decrease (i.e., deficit), increase (i.e., improvement), or absence of change in speed (Mann-Whitney test or unpaired t test according to the normality of the distribution). See also Figures S3 and S4.