Figure 6.
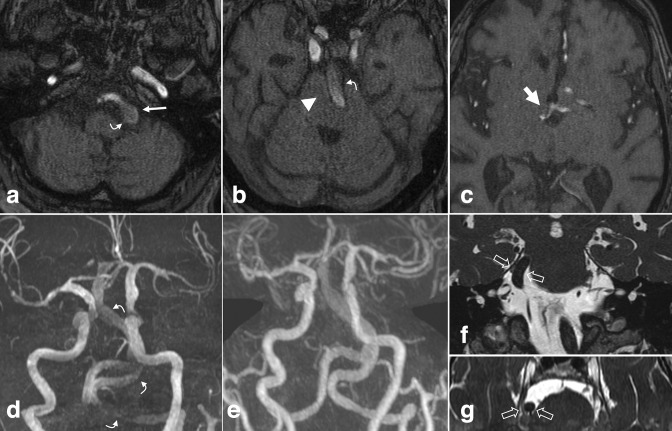
Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia. (a-c) Non-contrast axial TOF MRA and (d) 3D MIP reconstruction demonstrate diffuse distension, tortuosity, and elongation of the vertebrobasilar arteries. The BA measured up to 9 mm at the base. Note mass effect on the medulla and pons (b, arrowhead). The vertebrobasilar junction is laterally displaced beyond the left lateral margin of the clivus (a, small arrow). The height of the BA bifurcation is above the suprasellar cistern, abutting the hypothalamus (c, large arrow). Slow flow within the ectatic vessel attenuates flow-related enhancement and may mimic thrombus (a, b, d curved arrows). (e) Post-contrast 3D MIP from the concurrent head and neck MRA shows normal luminal patency. Coronal (f) and axial (g) high-resolution T2 weighted images in a different patient with dolichoectasia demonstrate displacement and compression of the cisternal trigeminal nerve due to a tortuous and lateralized BA (open arrows). BA, basilar artery; MIP, maximum intensity projection; MRA, MR angiography; TOF, time-of-flight.