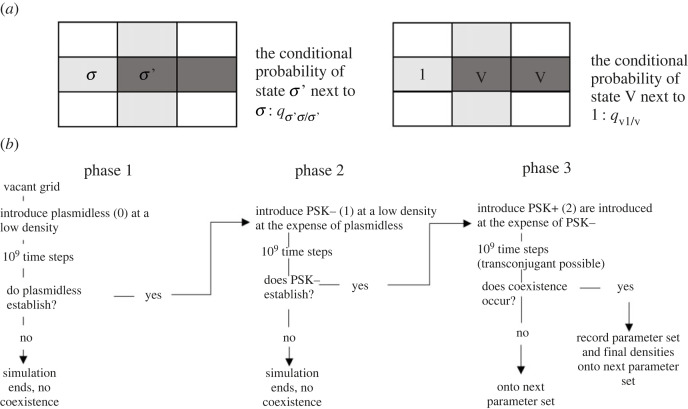
Figure 1.
Illustrates the principle of a doublet in a spatial lattice (a), as well as the procedure used to identify points of coexistence (b). A doublet is two adjacent sites in a lattice. For example, σ′σ forms a doublet where σ and σ′ are possible states (i.e. σ = 1 and σ′ = v). The quantity qσ′σ/σ′, captures spatial structure and is the conditional probability that given a site is in state σ′ it is adjacent to a site in state σ. For example, given a site is in state v, the probability it is in a doublet v1 is qv1/v. (b) outlines the three-phase approach to finding points of coexistence.