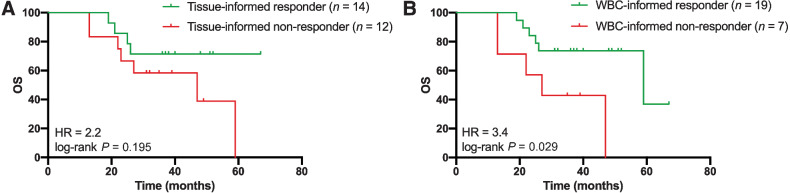
Figure 4.
Comparison of tissue-informed and WBC-informed approaches. Tissue-informed and WBC-informed approaches are compared for the 26 patients with plasma cfDNA, tumor tissue DNA, and WBC genomic DNA available prior to treatment. The molecular response was defined as ctDNA clearance over 98% after treatment compared with the initial baseline ctDNA measurement. A, Assessment of overall survival based on tissue-informed ctDNA analyses (HR = 2.2; 95% CI = 0.7–7.2; log-rank P = 0.195). B, Assessment of overall survival based on WBC-informed cfDNA analyses (HR = 3.4; 95% CI = 0.8–15.0; log-rank P = 0.029). cfDNA, cell-free DNA; ctDNA, circulating tumor DNA; HR, hazard ratio; WBC, white blood cell.