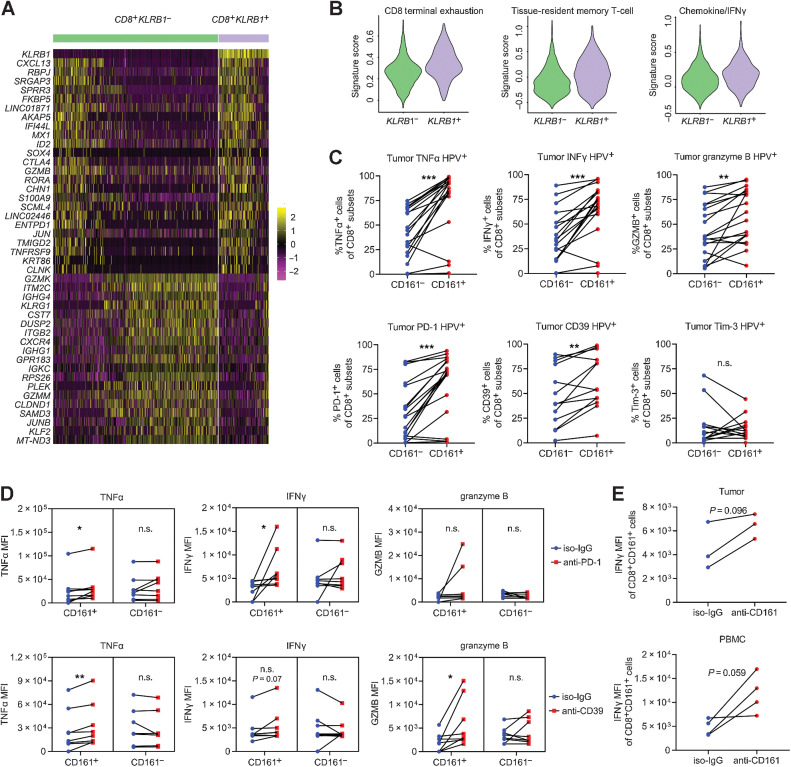
Figure 4.
The phenotype and function of CD161+ CTLs. A, Heat map displaying expression values of discriminative genes between KLRB1− and KLRB1+ CTLs (from clusters 0, 2, 3, and 9) based on the data from single-cell RNA sequencing. B, Scores for the terminal exhaustion signature, tissue-resident memory T-cell signature, and chemokine/IFNγ signature in KLRB1− and KLRB1+ CTLs based on the data from single-cell RNA sequencing. C, Coexpression of cytotoxic cytokines and inhibitory receptors on CD161− or CD161+ CTLs in OPSCC biopsies (n = 13–19) via flow cytometry, paired Student t test. D, MFI of cytotoxic cytokines coexpressed on CD161− or CD161+ CTLs treated with PD-1 or CD39 blocking antibodies in OPSCC biopsies (n = 7–8), paired Student t test. E, MFI of IFNγ coexpressed on CD161+ CTLs treated with CD161-blocking antibodies for 72 hours in HPV+ biopsies (n = 3) and blood samples (n = 4), paired Student t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. n.s.: no statistical significance.