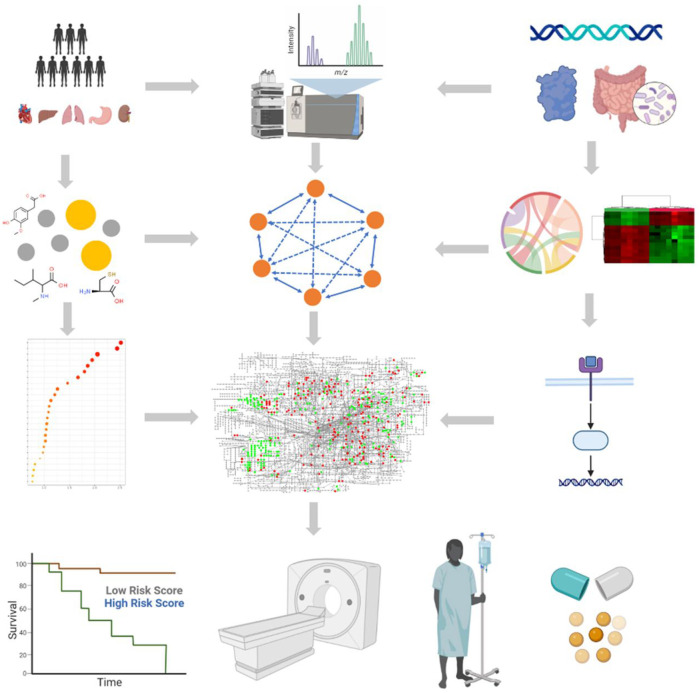
FIGURE 1.
Brief workflow of small-molecule metabolite-based functional metabolomics. The first stage involves experimental design, followed by the election of biological subjects, sample collection, preparation, and metabolite extraction. Metabolites are detected using specific detection techniques; data pre-processing is used to pre-process raw signals to produce data in a suitable format for subsequent statistical analysis; then, data normalization is used to reduce the system and technical bias; next, small-molecule metabolites are filtered and quantified for significant biomarkers of interest; statistical analyses and univariate and multivariate statistical analyses are used to identify significantly expressed metabolites; and finally, data are interpreted through biomarker discovery and functional interpretation. Multi-omics (genome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and microbiome) data are collected from patients and integrated to identify personalized functional signatures using complex and comprehensive network analysis. Next, the significantly expressed metabolites are subsequently linked to the biological context by enrichment and pathway analysis. Applications of small-molecule candidate metabolites for biomarker discovery, disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatments in clinical studies. Figure was drawn using BioRender and MetaboAnalyst.