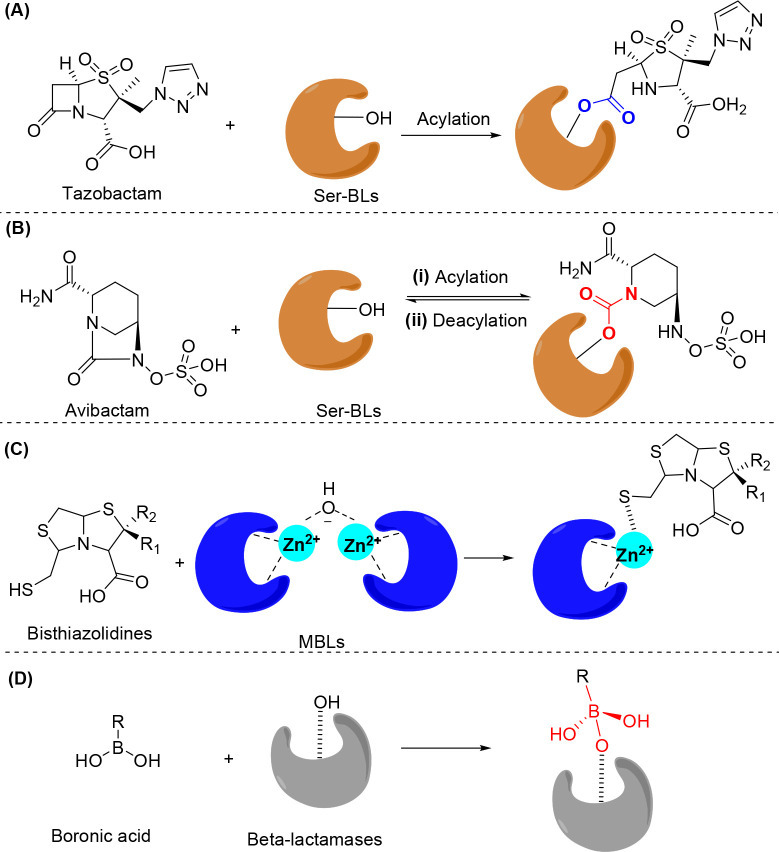
Figure 2.
General mechanism of β-lactamase inhibitors. (A) Acylation of serine-β-lactamases (Ser-BLs) by tazobactam to form an ester linkage. (B) Reversible acylation of Ser-BLs by avibactam to form a carbamoyl linkage. (C) Bisthiazolidines bind to the dizinc centers of metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) via a free thiol group. (D) Boronic acid inhibitors form tetrahedral intermediates with β-lactamases.