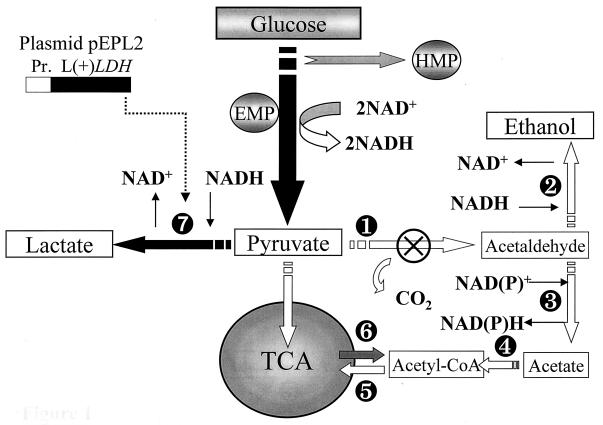
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the main pyruvate dissimilation pathways in K. lactis. EMP, Embden-Meyerhof pathway; HMP, hexose-monophosphate pathway; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle. Key enzymatic reactions at the pyruvate branch point are catalyzed by the following enzymes: ➊, pyruvate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.1; ⊗ indicates that this activity is absent in the K. lactic strain PMI/C1); ➋, alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.1); ➌, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.4 or EC 1.2.1.5); ➍, acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) synthetase (EC 6.2.1.1); ➎, acetyl CoA shuttle from the cytosol to mitochondria; ❻, acetyl CoA shuttle from mitochondria to the cytosol; and ❼, heterologous l-(+)-lactate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.27). Enzymatic reactions involved in anaplerotic syntheses have been omitted. Black arrows indicate the metabolic pathway leading to the production of lactic acid from glucose in heterolactic and homolactic strains PM6-7A(pEPL2) and PMI/C1(pEPL2), respectively. A schematic representation of the expression cassette [KlPDC1 promoter and l-(+) LDH gene] on the plasmid pEPL2 is also shown.