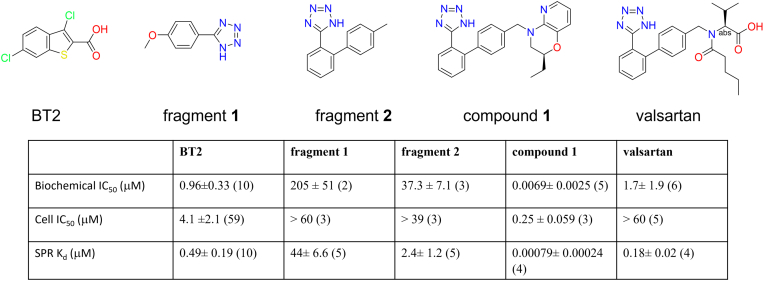
Figure 1.
Chemical structures and potencies of BCKDK inhibitors investigated in this study: BT2; fragment 1, identified in NMR-based fragment screen; fragment 2, identified by ligand-based virtual fragment screen; compound 1, identified by structure-based virtual expansion; valsartan, one of the most potent BCKDK inhibitors in the ARB family. The number of experiments performed are shown in parenthesis. Each experiment was a replicate of two inhibitor concentration series. The biochemical IC50 values were measurements at ATP concentration of 15 μM. The cell IC50 values were based on BCKDK-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous BCKD. SPR binding affinities were calculated from curve fitting to the responses of refractive index changes caused by inhibitors in solution binding to BCKDK immobilized on the SPR surface. Because of their fast off rates, the equilibrium Kd were calculated for BT2, fragment 1, and fragment 2. The more potent compound 1 and valsartan had measurable off rates, and their kinetic Kd were calculated. The absolute stereochemistry of compound 1 is undefined and arbitrarily assigned. ARB, angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker; BCKDK, branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase; BT2, 3,6-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.