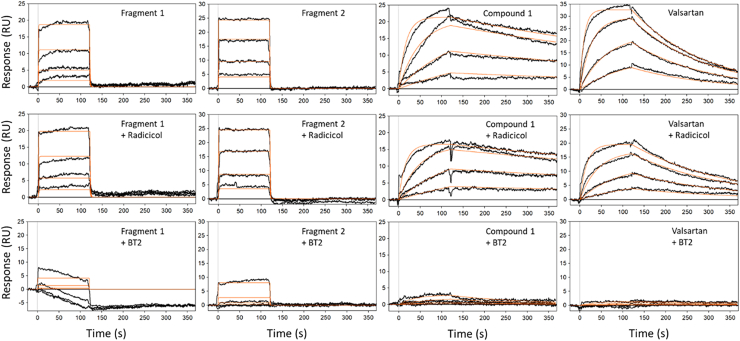
Figure 5.
Characterization of inhibitors binding to BCKDK by SPR.Top row, SPR sensorgrams of fragment 1, fragment 2, compound 1, and valsartan, respectively, binding to BCKDK superimposed with the equilibrium or kinetic curve fittings. Middle row, compounds binding in the presence of 20 μM ATP site competitor radicicol in the running buffer. Third row, competitive binding of ligands in the presence of 20 μM BT2. The compounds were tested in concentration series made with threefold dilution. The highest concentration tested was dependent on the potency of each compound: for fragment 1, it was 300 μM; for fragment 2, it was 20 μM; for valsartan, it was 2 μM; and for compound 1, it was 20 nM. The binding curves (black) were fit to a 1:1 Langmuir binding model (red) using Scrubber data analysis software. BCKDK, branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase; BT2, 3,6-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid; SPR, surface plasmon resonance.