Figure 3. Panel A, Targeting of Akt by Man-A Promotes Lymphoma Apoptosis.
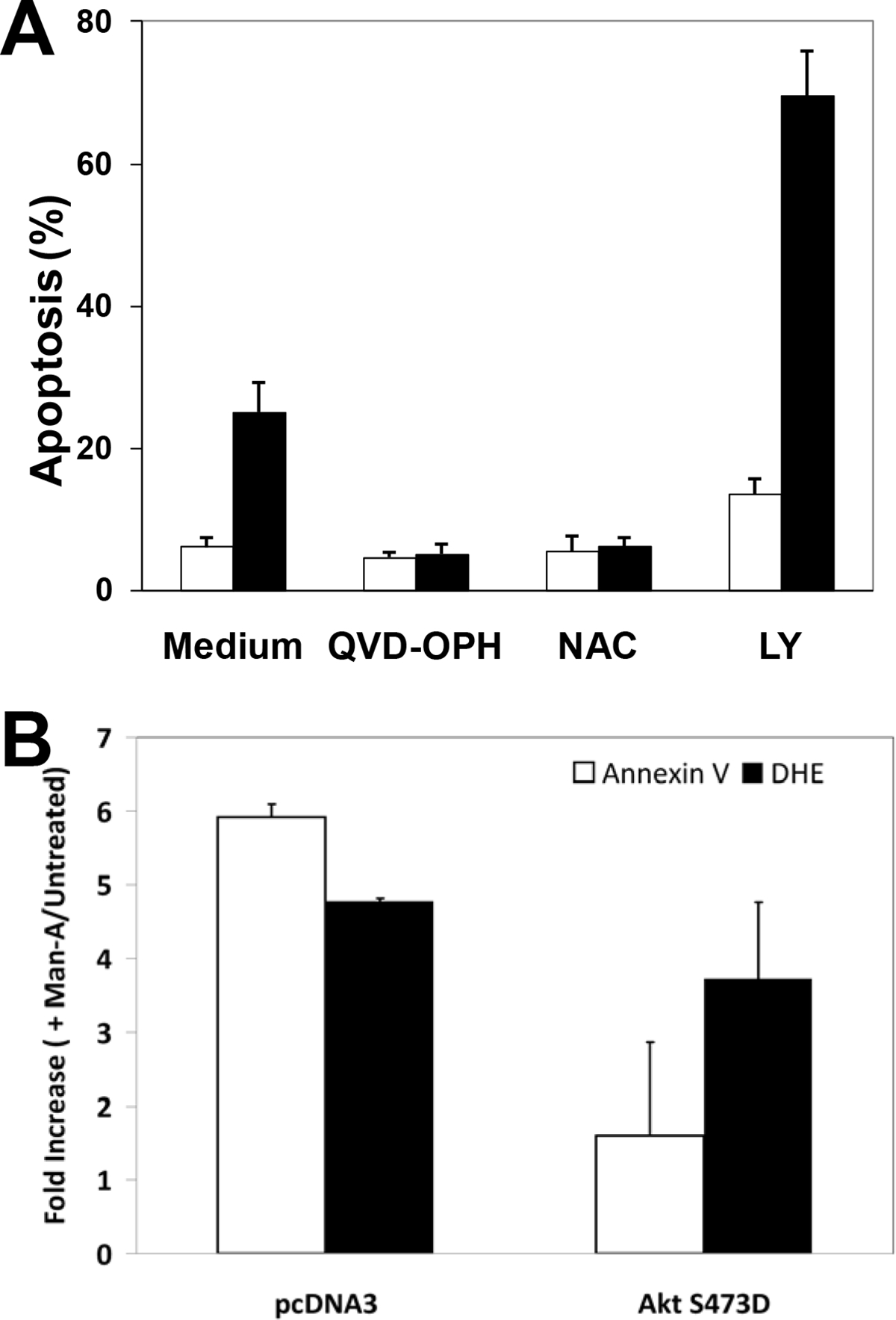
WEHI-231 cells were pre-treated with or without 10 μM QVD-OPH, 5 mM N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) or 10 μM LY294002 for 1 hour, followed by treatment with (■) or without (□) 4 μM Man-A for 2 hours. The label “Apoptosis (%)” denotes the percentage of sub-diploid nuclei measured after performing DNA content analysis as described in the Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as per cent Apoptosis and are representative of more than four separate, independent experiments. Panel B, Effects of Transiently Transfected AktS473D on Man-A Induced Apoptosis and Superoxide Production. WEHI-231 cells were transiently transfected with AktS473D/pcDNA3 using the Nucleofector method (Amaxa, See Materials and Methods) for 16h with the pMaxGFP cDNA in combinations with or without pcDNA3 vector alone or AktS473D constructed in pcDNA3. The cells were treated for 120 min with 4 μM Man-A. Apoptosis was assessed by measuring Annexin V binding to externalized phosphatidyl serine on GFP+/PI− cells, exactly as previously described by Sears et al. (Ref. 8). DHE probe was used to detect superoxide production as described in Materials and Methods and previously 8. Treatments were performed in triplicate and the data are expressed as the average fold increase (Treated / Untreated) in mean Annexin V-APC or DHE fluorescence ± SEM. The data are representative of at least two separate, independent experiments.
