Fig. 2. Setup of stimulation to target underlying trigeminal nerve anatomy.
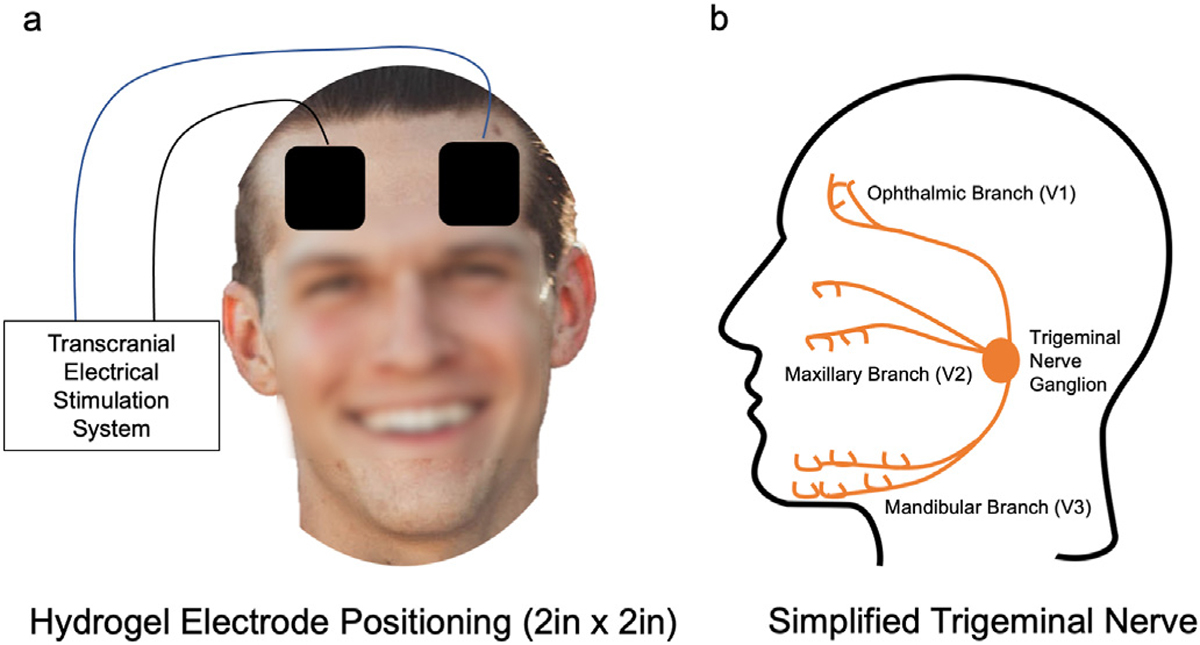
Overview of the electrode size and orientation for neurostimulation. Both tDCS and TNS utilized the same electrode position on the scalp (a), which allowed for stimulation of the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve. The electrical stimulator differed between tDCS and TNS. tDCS delivered a direct current stimulation, making the polarity important (anode on the right forehead, cathode on left). For TNS, the polarity placement was inconsequential due to the waveform. b) a simplified schema of the trigeminal nerve demonstrating three distinct branches and the stimulation target ophthalmic branch (V1).
