Figure 5. SPINK6 treatment suppresses viral growth and improves survival in mouse influenza infection.
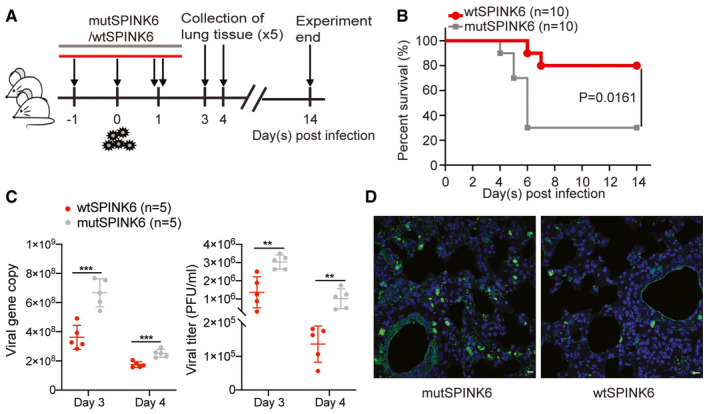
- Regime of the mouse experiment. Balb/c mice were a mouse‐adapted strain of pandemic H1N1 virus. At 24 h before inoculation, and 8, 24, and 36 h post‐inoculation, two groups of mice were intranasally administered with wtSPINK6 protein or mutSPINK6 protein. Ten mice treated with wtSPINK6 or mutSPINK6 were monitored daily for disease signs, body weight, and survival for 14 days. Five mice treated with wtSPINK6 or mutSPINK6 were sacrificed at 3 and 4 days after the viral challenge. Lung tissues were collected for the quantification of viral growth and immunofluorescence staining.
- Survival rates of mice treated with wtSPINK6 and mutSPINK6 were analyzed with Mantel–Cox test.
- Viral load and viral titer in the lung homogenates of mice treated with wtSPINK6 and mutSPINK6. Data represent mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Student’s t‐test.
- Mouse lung tissues are applied to immunofluorescence staining to identify the viral NP‐positive cells (green). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). Representative confocal images of virus‐infected cells in the indicated mice. Scale bar, 10 µm.
