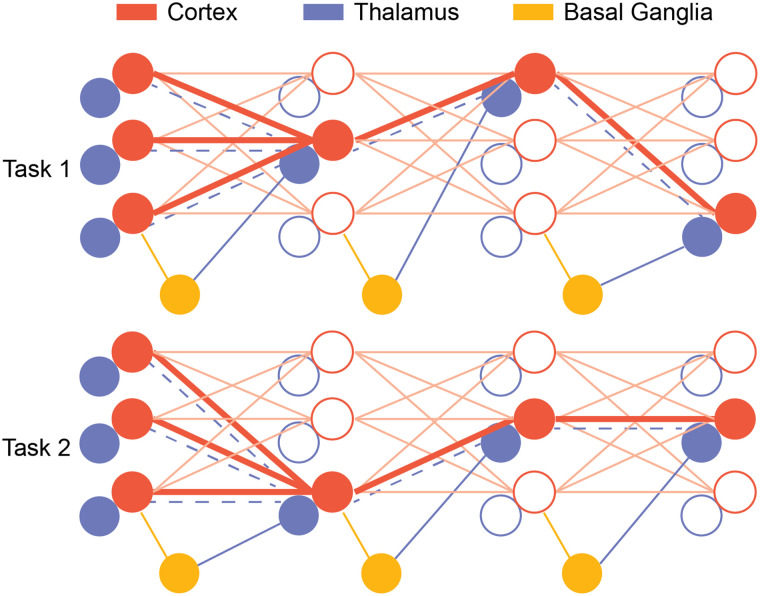
Figure 4. .
A thalamocortical architecture with interaction with BG for continual learning. During task execution, BG selects thalamic neurons that amplify the relevant cortical subnetwork. This protects other parts of the network that are important for another context from being overwritten. When the other task comes, BG selects other thalamic neurons and since the synapses are protected from the last task, animals can freely switch from different tasks without forgetting the previous tasks. Furthermore, as the corticothalamic synapses learn how to select the right thalamic neurons in a different context (blue dashed line), task execution can become less BG dependent.