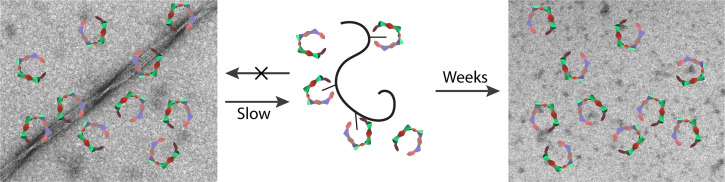
Fig. 17.
Putative schematic mechanism of fibril dissociation by MTs. Time-dependent EM analysis allow the following conclusions: Binding of MTs to the fibrils of disease-associated proteins, such as Aβ, does not disrupt the fibrils. However, in the presence of excess MT, binding to the small fraction of soluble protein molecules does not allow them to re-bind to the fibrils, slowly shifting the equilibrium toward dissociation.