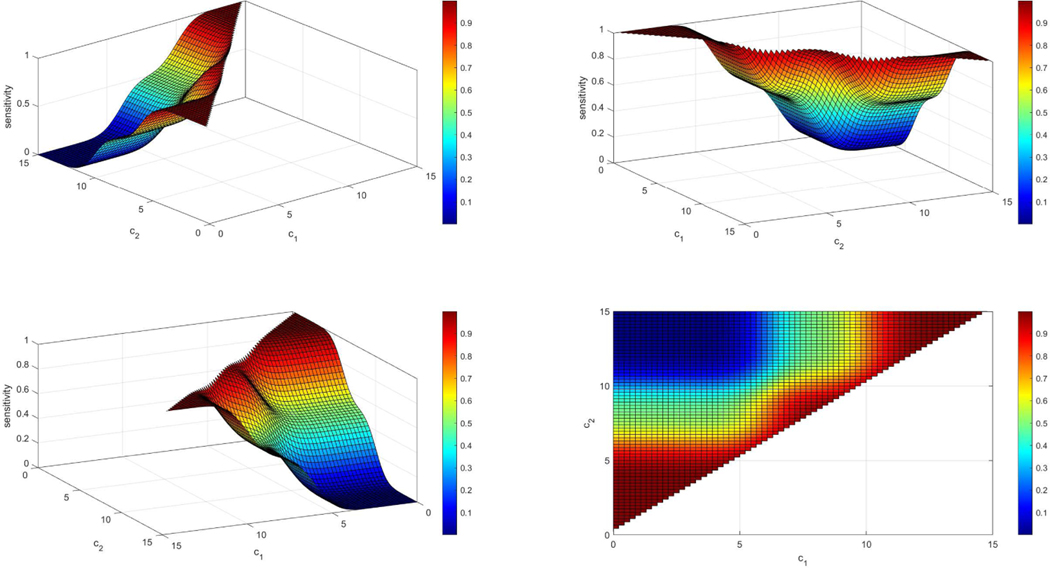
Figure 4.
Example of a sensitivity surface when the density of the controls is N(8,1) and the density of the cases is a two component normal mixture: 0.5N(6, 1) + 0.5N(10, 1). The sensitivity plot is given under four different angles (panels above) for better visualization. We observe that when c1 is very small and c2 is very large then the sensitivity yields very low values since the mass of both densities is low below c1 and beyond c2. In addition, if c1 is very close to c2 then we expect that almost all individuals that are diseased will be categorized as such since it is very likely that they will not be between c1 and c2 and thus the sensitivity for those cutoffs is very high (red regions).