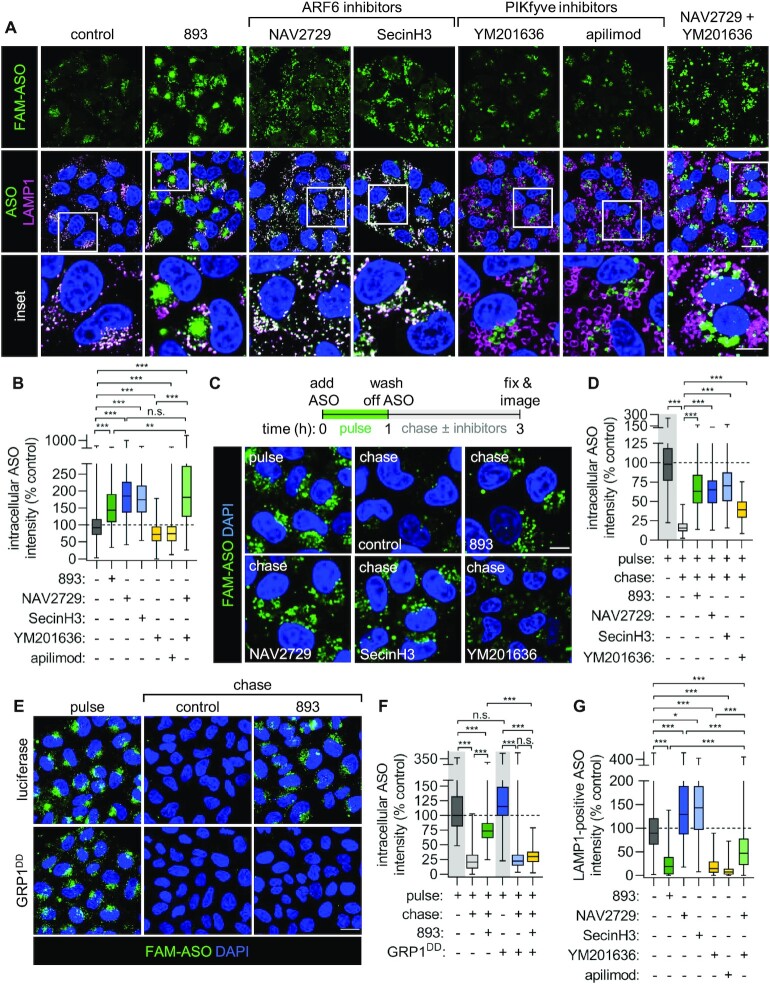
Figure 3.
Simultaneous PIKfyve and ARF6 inhibition is both necessary and sufficient to recapitulate the effects of SH-BC-893 on ASO uptake and localization. (A) FAM-tagged cEt 3–10–3 ASO and LAMP1 localization in HeLa cells treated with SH-BC-893 (5 μM), NAV2729 (12.5 μM), SecinH3 (30 μM), YM201636 (800 nM), apilimod (100 nM), or both NAV2729 and YM20636 for 6 h. (B) Quantification of the total intracellular ASO fluorescence intensity from the images in (A). At least 100 cells were quantified from each of 3–4 independent experiments. Because the data is not normally distributed, a Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA was used with Dunn's test to correct for multiple comparisons. ***P < 0.001. (C) HeLa cells were pulsed with FAM-tagged 3–10–3 cEt ASO (2 μM) for 1 h, washed, and then chased in media containing vehicle (DMSO), SH-BC-893 (5 μM), NAV2729 (12.5 μM), SecinH3 (30 μM), or YM201636 (800 nM) for 2 h prior to imaging. (D) Quantification of the intracellular ASO fluorescence of cells in (C). At least 100 cells were quantified from each of two independent experiments. Because data is not normally distributed, a Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA was used with Dunn's test to correct for multiple comparisons. ***P < 0.001. (E) HeLa cells expressing luciferase or GRP1DD were subjected to an ASO pulse-chase as in (C). (F) Quantification of the intracellular ASO fluorescence intensity in (E) performed as in (D). Scale bars, 20 μm (A and E) or 10 μm (inset in A and in C). (G) As in (B), except ASO fluorescence intensity within LAMP1-positive pixels is measured. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.