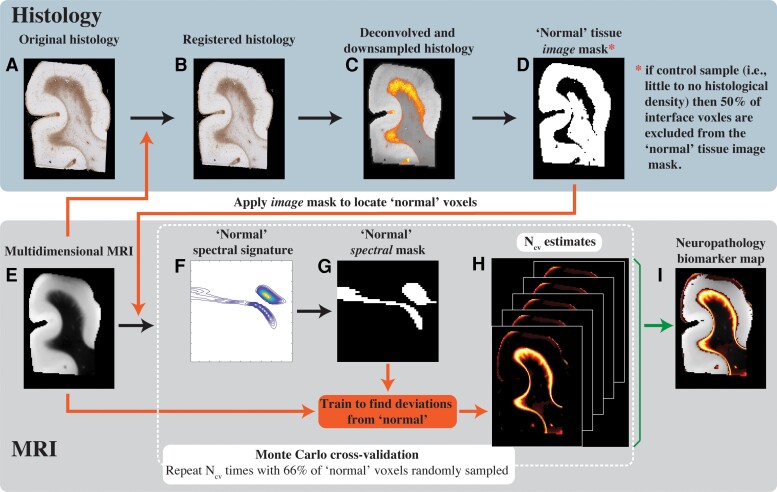
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the proposed anomaly detection framework. (A) The original GFAP histological image is processed in two steps: (B) co-registration to the MRI data set and (C) subsequent deconvolution and downsampling to match the MRI resolution. (D) This GFAP density image is then thresholded, inverted and used as an image domain mask for normative brain voxels on the (E) multidimensional MRI data. A Monte Carlo cross-validation procedure is used to create Ncv = 1000 multiple random splits of 66% and 34% of the normal-appearing voxels into training and validation data, respectively, resulting in a 1000 (F) normative spectral signatures, each of which is binarized to obtain (G) spectral masks of normative brain. To detect anomalies, the normative spectral mask is inverted and is used on the full multidimensional data to directly obtain (H) Ncv = 1000 versions of abnormal signal component maps, which are then averaged to yield the final (I) neuropathology MRI biomarker map.