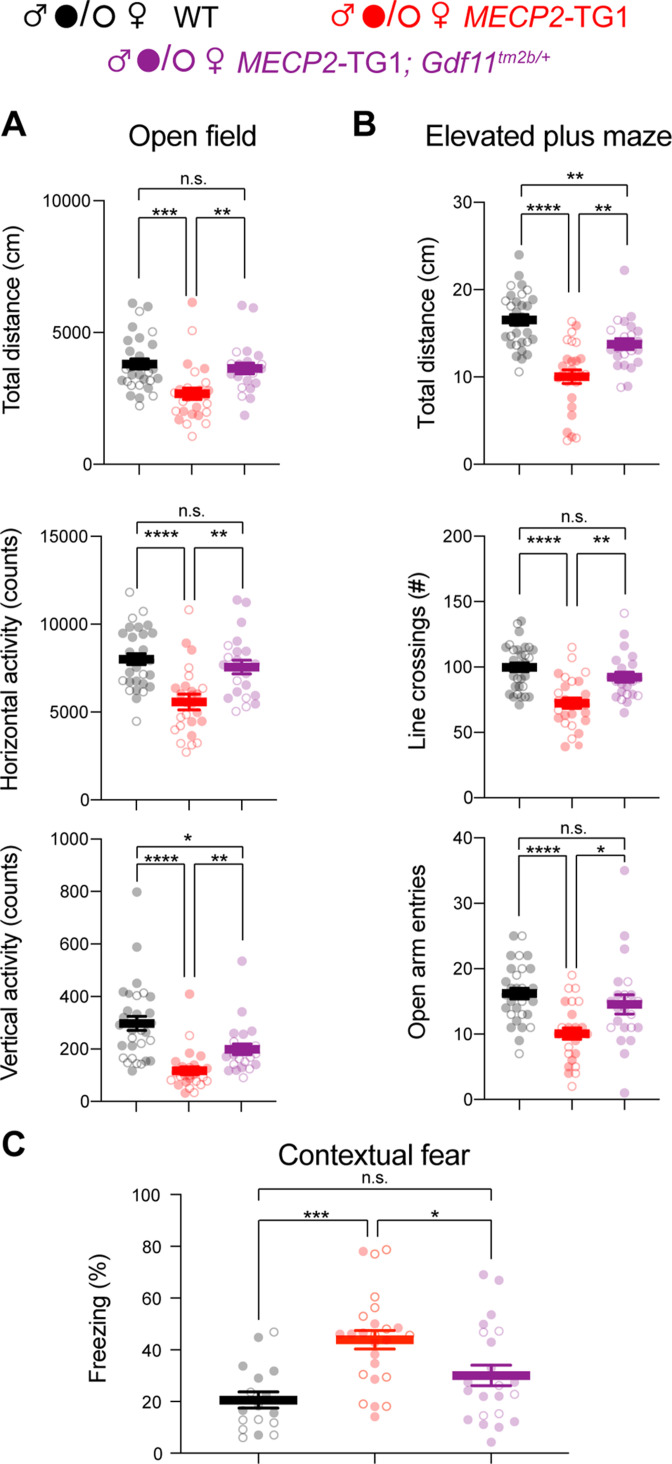
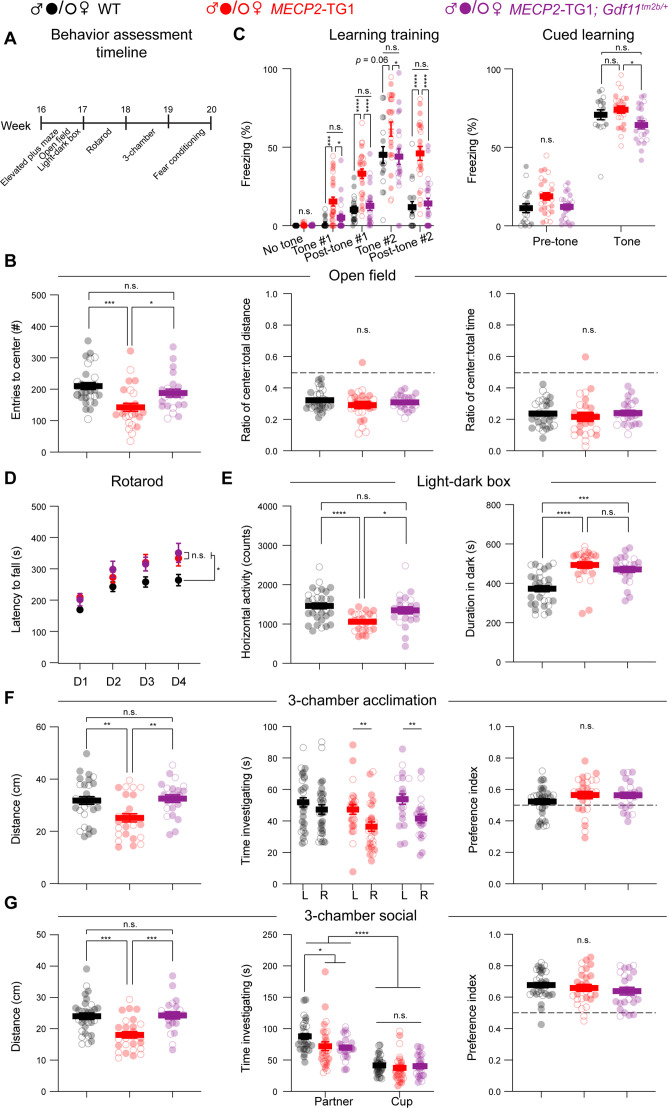
Figure 2. Genetic reduction and normalization of Gdf11 dose ameliorates several behavioral deficits in MECP2-TG1 mice.
Behavioral characterization of MECP2-TG1, MECP2-TG1; Gdf11tm2b/+ double mutants, and their respective wild-type littermate controls was performed beginning at 16 weeks of age. (A) Open-field assessment of locomotion and activity. (B) Elevated plus maze assay measures of movement and anxiety-like behaviors. (C) Learning assessment using contextual fear-conditioning. Greater freezing indicates better memory of the context. Central estimate of data is shown as mean ± sem. Closed circles denote male mouse data points and open circles denote female mouse data points. For all open field and elevated plus maze (A,B), n=30 wild-type mice (19 male, 11 female); n=26 MECP2-TG1 mice (14 male, 12 female); and n=22 MECP2-TG1; Gdf11tm2b/+ mice (16 male, 6 female). For fear conditioning assay (C), n=17 wild-type mice (9 male, 8 female); n=25 MECP2-TG1 mice (13 male, 12 female); and n=22 MECP2-TG1; Gdf11tm2b/+ mice (16 male, 6 female). All data were analyzed using a Welsch one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc multiple comparisons, and raw measurements are provided in Figure 2—source data 1. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, and **** p<0.0001.