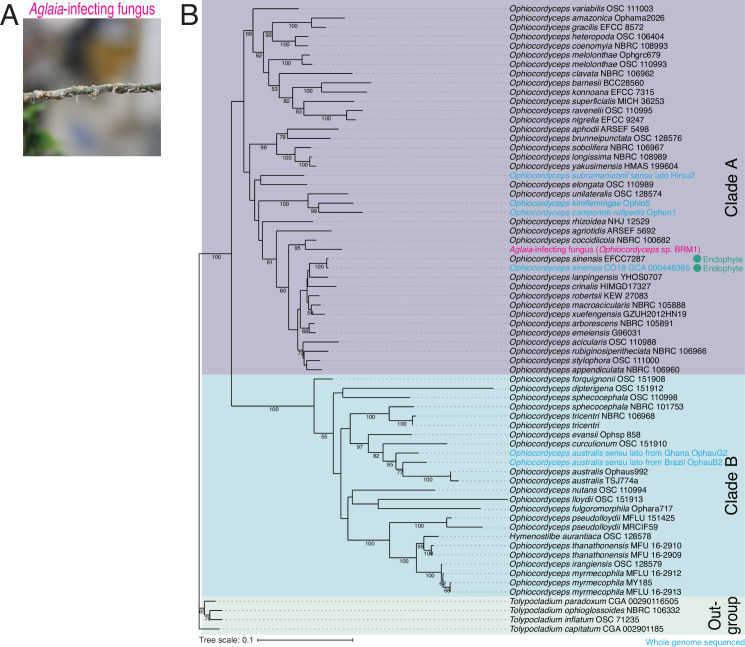
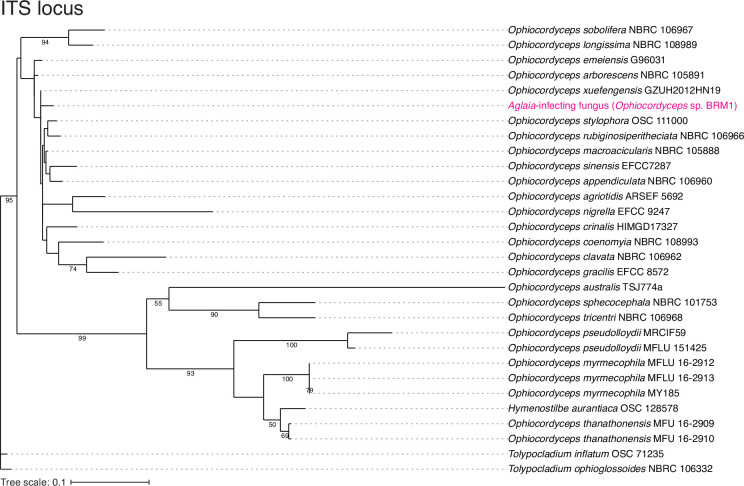
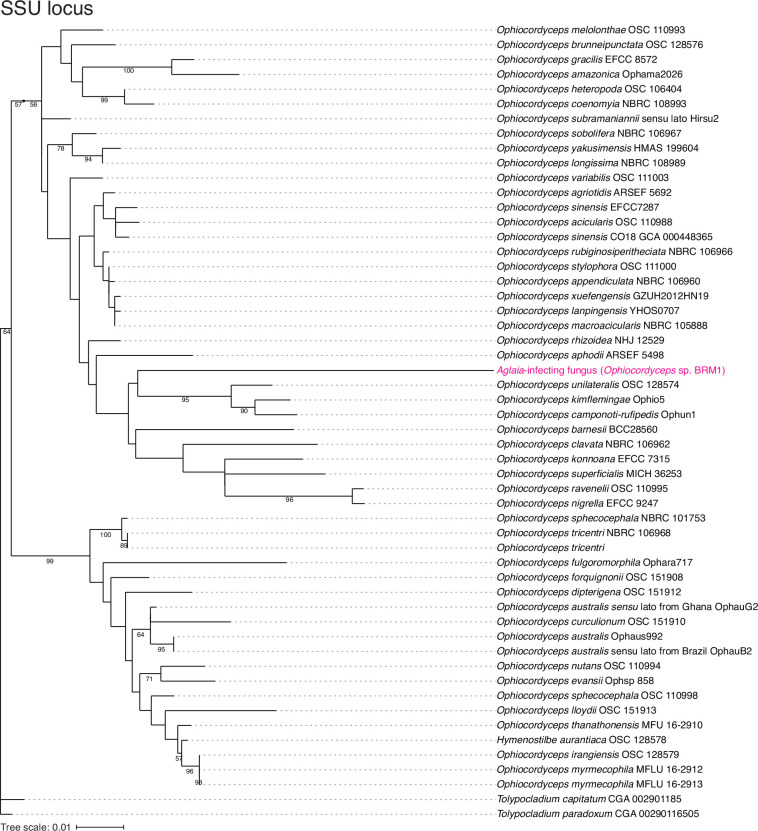
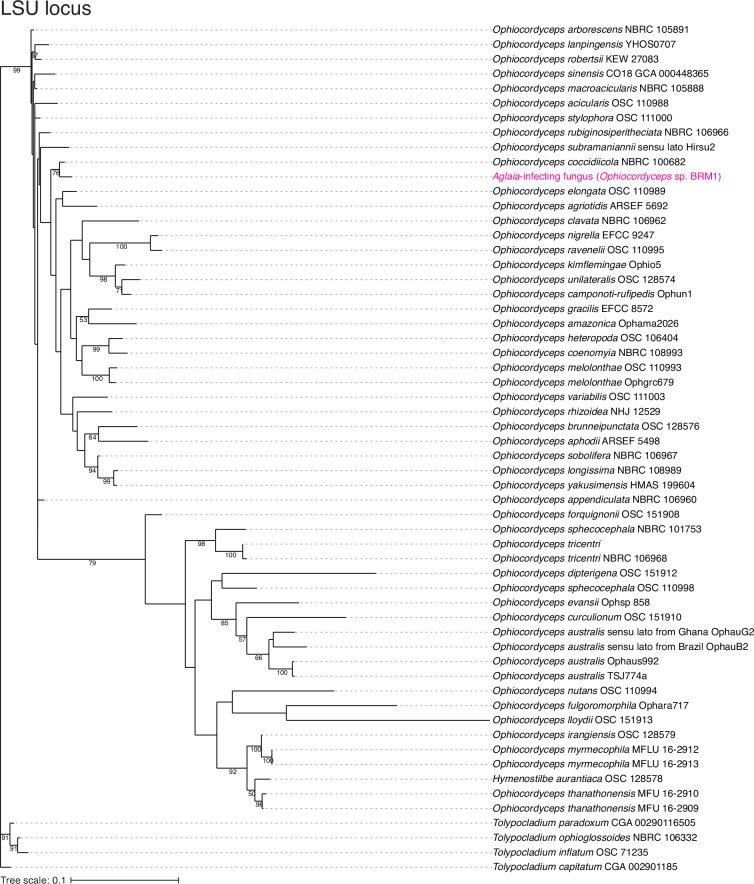
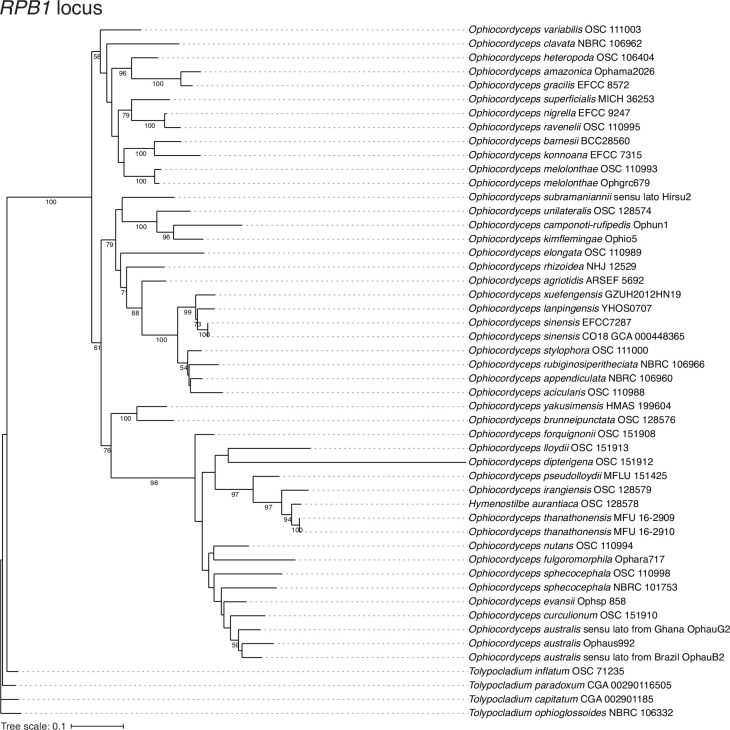
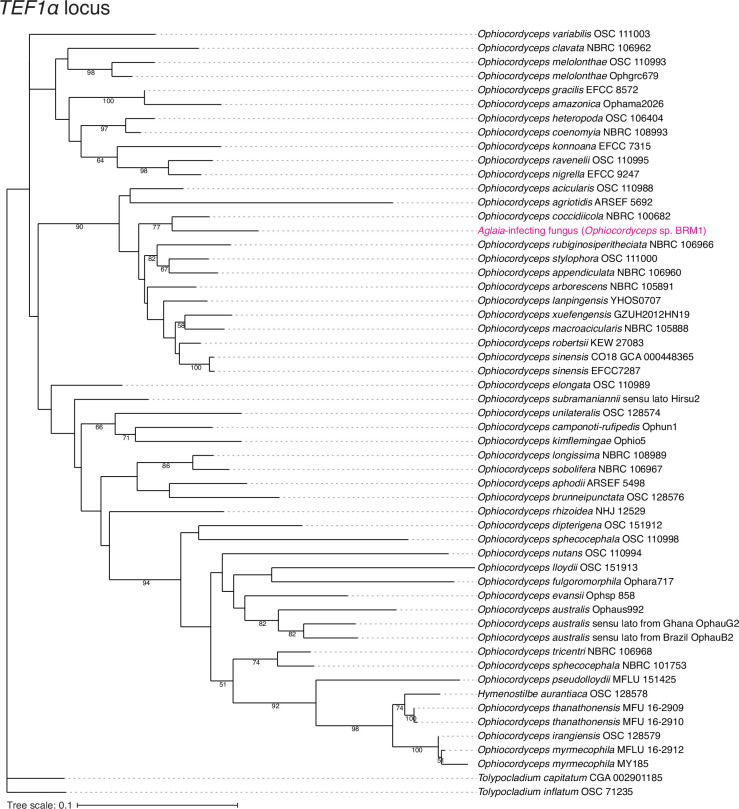
Figure 1. Identification of Aglaia-parasitic Ophiocordyceps sp. BRM1.
(A) Image of a parasite fungus growing on Aglaia odorata. (B) Multilocus phylogenetic tree of Ophiocordyceps species generated from maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of ITS, SSU, LSU, RPB1, and TEF1α sequences. Tolypocladium species were used as outgroups. The best DNA substitution models of ITS, LSU, SSU, RPB1, and TEF1α were calculated as TIM3ef + G4, TIM1 + I + G4, TIM3ef + I + G4, TrN + I + G4, and TIM1 + I + G4, respectively. Numbers on branches are percent support values out of 1000 bootstrap replicates. Only bootstrap values greater than 50% support are shown. Endophytes are highlighted with green dots.