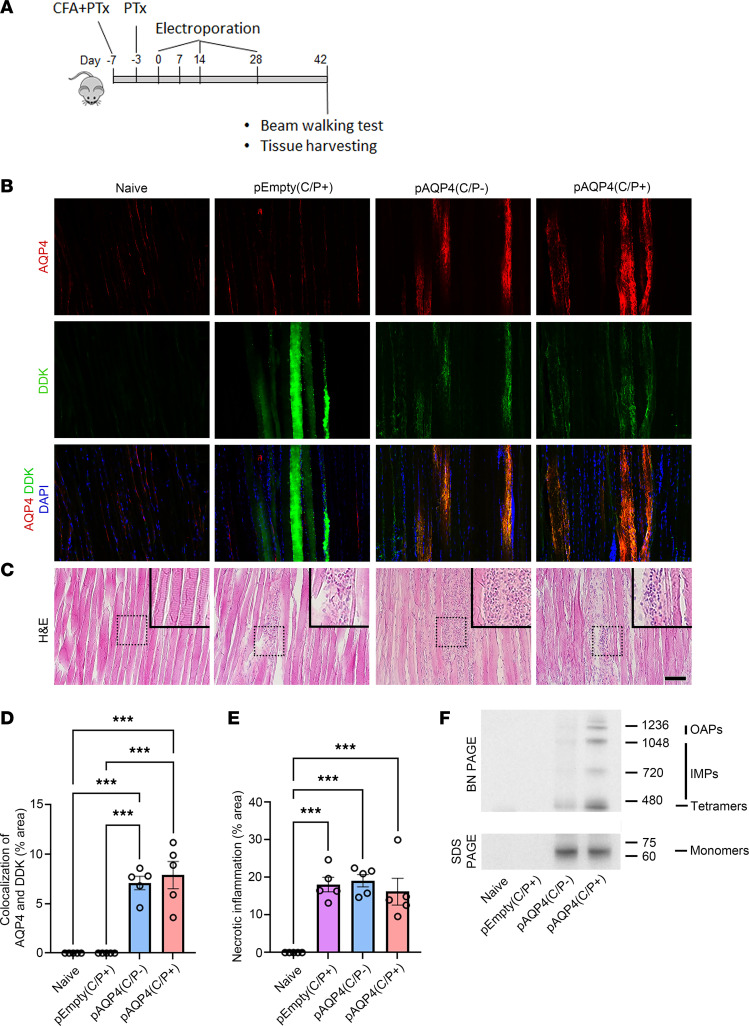
Figure 1. In vivo electroporation triggers AQP4 overexpression in skeletal muscle.
(A) Experimental design. Mice were pretreated with CFA and PTx. Then animals received in vivo electroporation of pAQP4 or pEmpty at the left tibialis anterior muscle. Electroporation was performed at days 0, 14, and 28. Animals were culled at day 42. (B) Coimmunostaining for AQP4 and Myc-DDK in skeletal muscle. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. (C) H&E staining for skeletal muscle. Images are representative of the longitudinal section of the tibialis anterior muscle from 5 mice per group. Insets are higher-magnification photomicrographs showing immune cell infiltration. (D) Percentage area of AQP4 and Myc-DDK colocalization in the muscle. (E) Percentage area of necrotic inflammation in the muscle. (F) Western blot analysis of protein from skeletal muscle cell lysate separated in native form by BN-PAGE, and in denatured form by SDS-PAGE. Top: BN-PAGE shows the expression of fusion proteins consisting of Myc-DDK and AQP4 OAPs, IMPs, and tetramers in the muscle after electroporation with pAQP4. Bottom: SDS-PAGE shows the expression of a fusion protein (60 kDa) consisting of Myc-DDK and AQP4 M23 monomers in the muscle after electroporation with pAQP4. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 5 per group. ***P < 0.001, 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test. Scale bar: 50 μm. Original magnification, ×400 (insets).