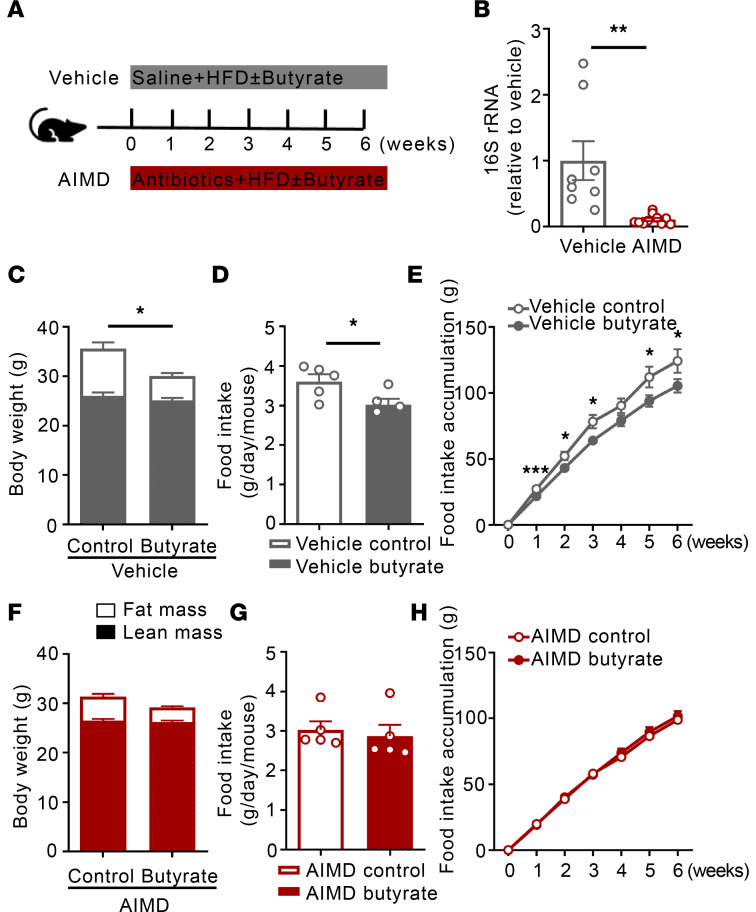
Figure 1. Dietary butyrate reduces food intake and attenuates HFD-induced weight gain dependent on gut microbiota.
(A) Mice underwent AIMD or received saline (vehicle) for 6 weeks while being fed an HFD without or with 5% (weight by weight [w/w], i.e., on average 0.12 g per day per mouse) sodium butyrate. (B) At the end of the treatment, fresh feces were collected and bacterial DNA was quantified by 16S rRNA gene amplification by PCR (n = 8–9). (C and F) Body composition was measured by MRI (n = 8). (D and G) The average food intake per day throughout the whole intervention period was calculated (n = 5). (E and H) The cumulative food intake was calculated (n = 5). Data are shown as means ± SEM; statistical significance between 2 groups was determined with 2-tailed Student’s unpaired t test. For data represented in the line graphs showing the changes over time for a continuous variable, statistical significance between 2 groups at each time point was determined using 2-tailed Student’s unpaired t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; AIMD vs. vehicle in B or Butyrate vs. Control in C–H.