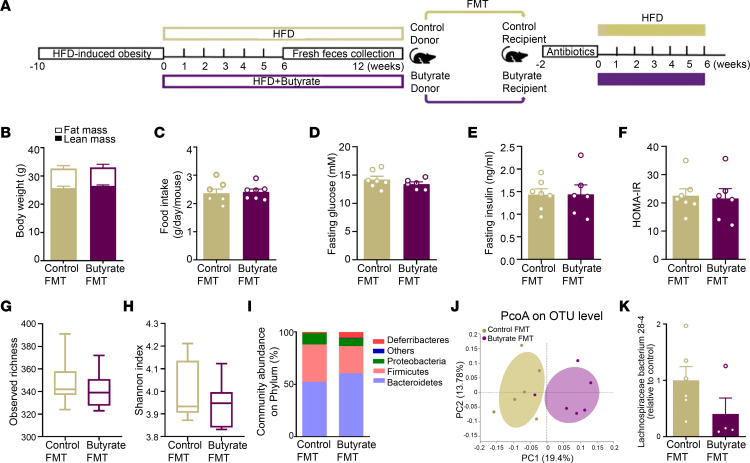
Figure 6. FMT from butyrate-treated obese donor mice does not attenuate weight gain, ameliorate metabolic health, or enrich Lachnospiraceae bacterium 28-4 in recipient mice.
DIO mice fed an HFD without or with 5% (w/w) butyrate treatment for 6 weeks. (A) After this, fresh feces were collected weekly and used for FMT to gut microbiota-depleted recipient mice that were fed an HFD for 6 weeks. (B) Body composition was calculated by MRI at the end of the study (n = 6–7). (C) The average food intake per day throughout the intervention period was calculated (n = 6–7). (D) Fasting plasma glucose (n = 6–7) and (E) insulin (n = 6–7) were measured and used to calculate (F) HOMA-IR (n = 6–7). Cecum bacterial DNA was collected and (G) the observed richness of taxonomy (n = 6) and (H) Shannon diversity (n = 6) of gut microbiota were calculated by 16S rRNA-Seq analysis. (I) The composition of abundant bacteria on phylum (n = 6) and (J) PCoA plot of unweighted UniFrac distances on OTU levels (n = 6) were calculated. (K) The abundance of Lachnospiraceae bacterium 28-4 was quantified by real-time PCR (n = 4–6). Data are shown as means ± SEM for B–F and K or box plot with whiskers at min/max for G and H. Statistical significance between 2 groups was determined with 2-tailed Student’s unpaired t test; For data represented in the line graphs showing the changes over time for a continuous variable, statistical significance between 2 groups at each time point was determined using 2-tailed Student’s unpaired t test.