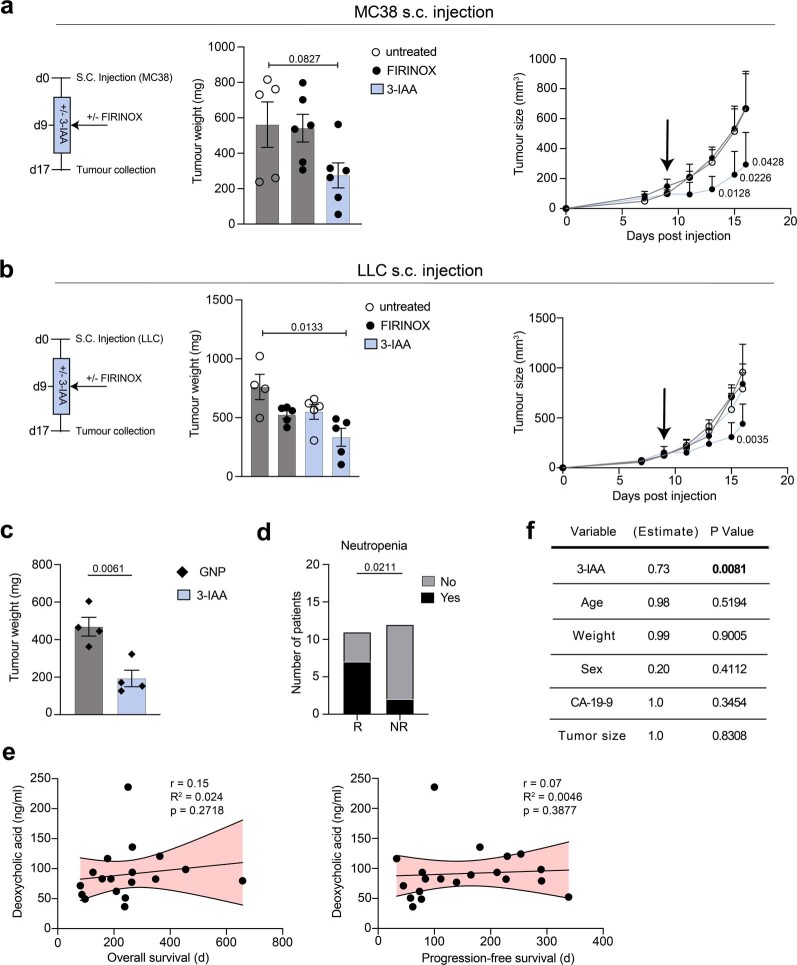
Extended Data Fig. 9. A 3-IAA and chemotherapy combination is effective in the treatment of colorectal and lung cancer cell lines.
a,b, The MC38 colorectal cancer cell line (n = 5 or 6; a) or LLC lung cancer cell line (n = 4 or 5; b) was subcutaneously injected and mice were treated +/− FIRINOX and +/− 3-IAA (500 mg/kg) orally. Tumours were measured every other day and tumour weight was scaled to day 17 of experiment. c, Orthotopic KPC tumours were established and SPF mice were treated with GNP once +/− 3-IAA (500 mg/kg; n = 4 each). Tumour weight was assessed seven days after chemotherapy (d18). d, Statistics show the event of neutropenia (<1,5*109/l) during the first 6 cycles of chemotherapy in patients from the Hamburg cohort responding or not responding to the chemotherapy (n = 11 R and 12 NR). e, DCA concentration was measured after two to three chemotherapy cycles in the serum of patients from the Hamburg cohort and was correlated with PFS (n = 20) or overall survival (n = 18). Each symbol represents one patient. f, Univariate Cox proportional hazard models were used to determine the effects of indicated variables on PFS in the Hamburg cohort. One experiment (b) or one out of two individual experiments (a) is shown. Error bars indicate SEM, significant p-values are indicated and were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test (a, left statistic), Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s (b, left statistic) post-hoc test, mixed-effects analysis followed by Dunnett’s post-hoc test (a and b, right statistic), two-tailed t-test (c), two-sided chi-square test (d), simple linear regression and Pearson’s r (e) or Cox regression (f).