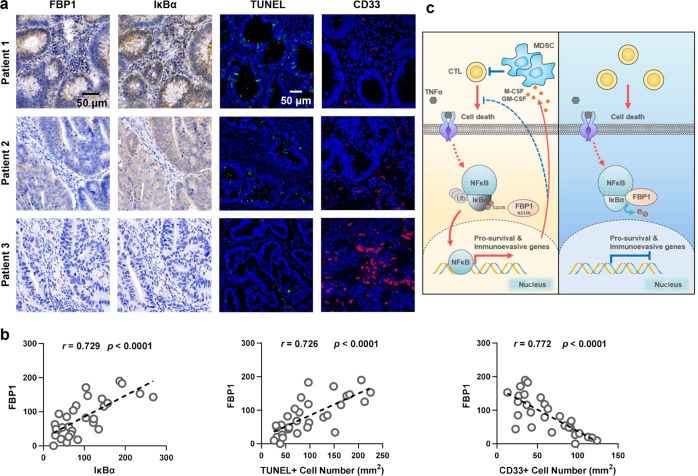
Fig. 5. FBP1 expression inversely correlates with NF-κB activation, cell survival, and MDSC infiltration in human CRC tumors.
a, b IHC staining with anti-FBP1 and anti-IκBα antibodies, IF staining with anti-CD33 antibody and TUNEL staining of 30 specimens from patients with CRC were performed. Representative images of IHC, IF and TUNEL staining of three specimens are shown (a). Semi-quantitative scoring (using a scale from 0 to 300) was carried out between FBP1 and IκBα. IHC staining scores and TUNEL+ cells or CD33+ cells of the CRC specimens were compared (b, Pearson’s correlation test). c Schematic model of the suppressive role of FBP1-mediated IκBα dephosphorylation in tumorigenesis. Upon TNFα stimulation, FBP1 interacts with and dephosphorylates IκBα, thereby inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Inactivated NF-κB suppresses tumorigenesis by sensitizing tumor cells to inflammatory stresses produced by CTLs and preventing the mobilization of MDSCs (Right panel). N213K mutation disrupts the interaction between FBP1 and IκBα, thereby restoring NF-κB activation and subsequent expression of prosurvival genes and MDSC-mobilizing genes, which promotes cell survival, MDSCs mobilization and tumorigenesis (Left panel).