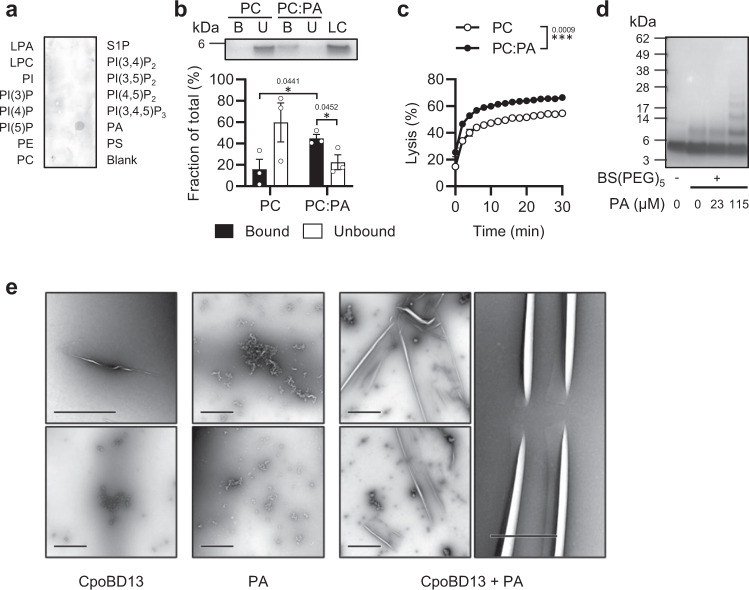
Fig. 2. CpoBD13 binds and preferentially lyses liposomes containing the anionic phospholipid phosphatidic acid.
a Immunodetection of CpoBD13-HA overlayed on a PIP Strip shows specific binding to PA. b Liposome pulldown comparing the binding of CpoBD13 to PC only and PC:PA (95:5 molar ratio) liposomes. Bound (B, black) and Unbound (U, white) fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis and colloidal Coomassie staining. The intensities of the bands were calculated as a fraction of a 1 µg loading control (LC) using ImageJ software. Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 3. *P < 0.05, two-tailed unpaired t test. c Liposome lysis of calcein-encapsulated PC only (white) and PC:PA (black) liposomes by 20 µM CpoBD13 over 30 min. Lysis was calculated as a fraction of a 100% lysis control using 0.1% Triton X-100. Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 3. ***P = 0.0009, two-way ANOVA. d Chemical crosslinking of CpoBD13 using BS(PEG)5 in the presence of various concentrations of PA followed by SDS-PAGE analysis and colloidal Coomassie staining. Image is representative of three independent experiments. e TEM images of CpoBD13 alone, PA alone or CpoBD13:PA complexes (scale bars represent 1 µm). Images are representative of two independent experiments. (a–d) Source data are provided as a Source Data file.