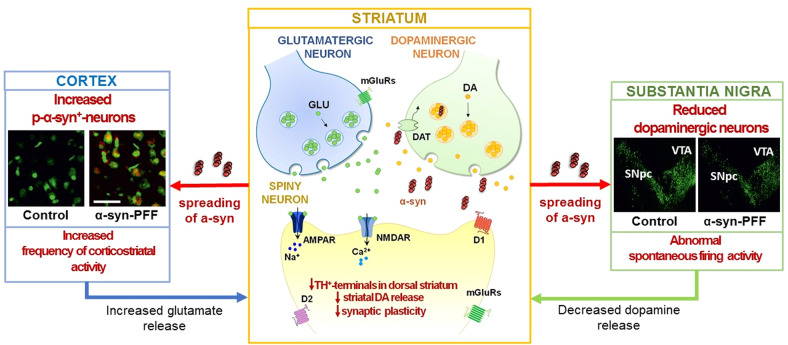
Fig. 3. Presynaptic and postsynaptic dysfunctions induced by intrastriatal injection of α-syn-PFFs in the rat model.
Left panel: in the cortical areas, a consistent proportion of p-α-syn+ neurons was detected in α-syn-PFFs-injected rats. Analysis of spontaneous synaptic currents indicates an increased frequency of the spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current in target neurons of the dorsal striatum that brings to a state of hyperglutamatergic activity. Right panel: the SNpc in α-syn-PFF rats presents a reduced number of dopaminergic neurons as displayed by a decrease of TH+-immunofluorence, associated with an abnormal increase in spontaneous firing activity. Center panel: in the dorsolateral striatum, α-syn-PFFs injection leads to profound alterations of the corticostriatal long-term plasticity, in the SPNs. A significant decrease of TH+ fibers and a reduced release of endogenous dopamine from SNpc terminals are also observed.