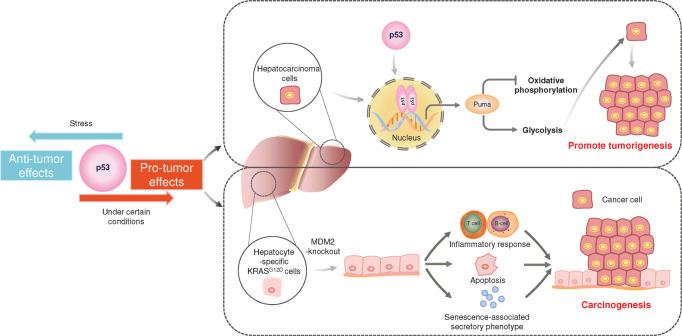
Fig. 3.
Pro-tumor effect of p53. In general, p53 is thought to have tumor suppressive effects, but in some cases, p53 promotes tumor growth. In hepatocellular carcinoma cells, p53 transcription activates the expression of Puma, which causes shift in mitochondrial energy metabolism from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis, thereby promoting tumorigenesis. In hepatocyte-specific KRASG12D cells knockout of MDM2 to activate p53. Accumulated p53 increased inflammatory responses, hepatocyte apoptosis, and senescence-associated secretory phenotypes that promote carcinogenesis