Fig. 1. The human DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system.
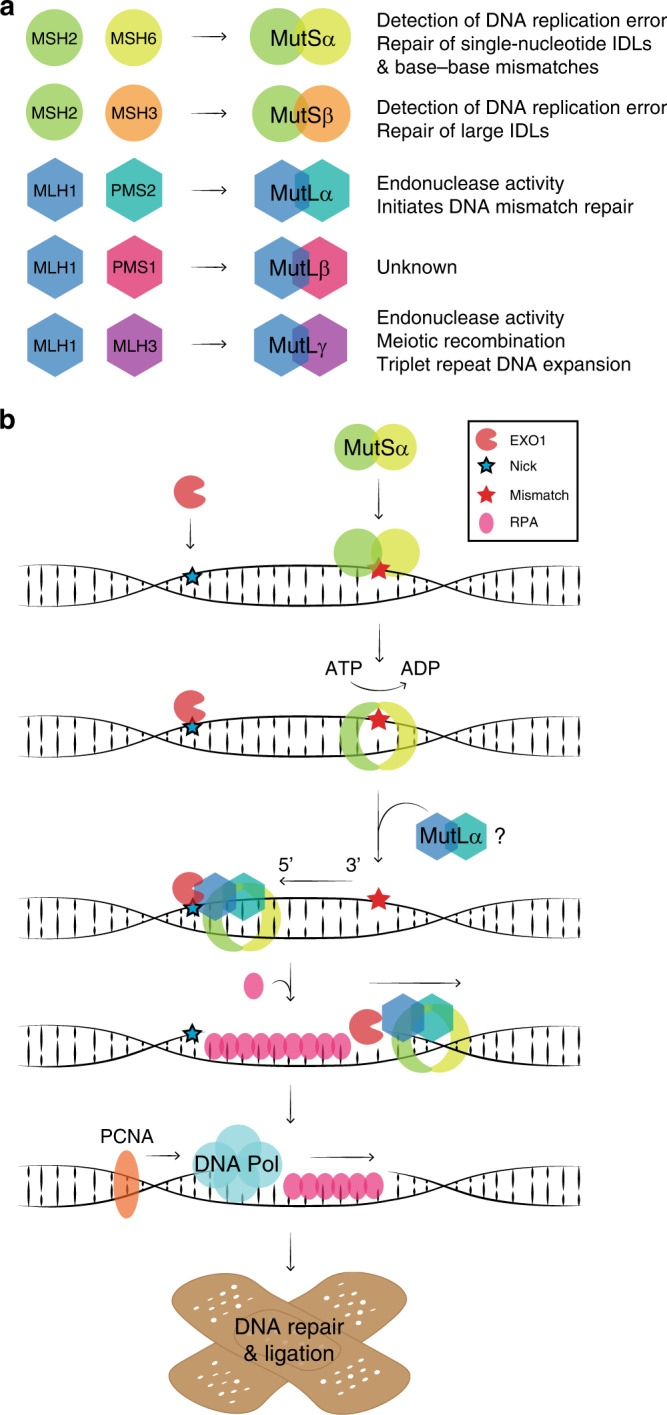
a The MSH2 protein forms dimers with MSH6 (MutSα) and MSH3 (MutSβ). The MLH1 protein forms dimers with PMS2 (MutLα), PMS1 (MutLβ) and MLH3 (MutLγ). Heterodimer functions are listed. IDL, insertion/deletion loop. b A schematic illustration of the 5’ to 3’ MMR pathway. EXO1 binds a nick in the newly synthesised DNA strand 5’ to the mismatch. MutSα recognises the mismatch and undergoes an ATP-dependent conformational change, which locks the complex around the DNA to form a sliding clamp. MutSα moves along the DNA strand and interacts with MutLα, which further binds the DNA. MutSα/MutLα binds EXO1 and moves in the 5’ to 3’ direction allowing for the excision of the mismatch by EXO1. RPA protects the unpaired strand until the DNA polymerase bound to PCNA repairs the strand, after which the DNA ligase seals off any remaining nicks (not shown).
