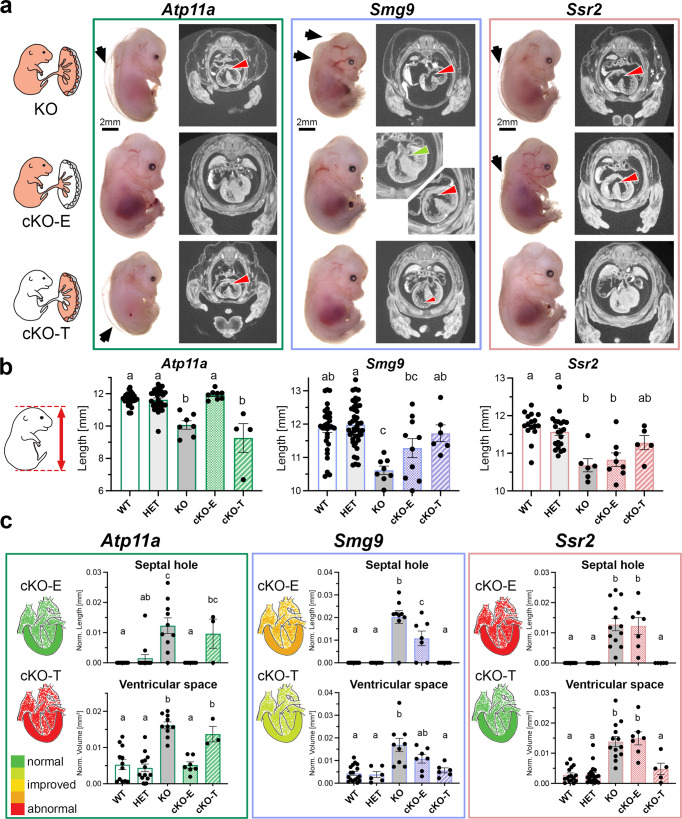
Fig. 4. Conditional knockout analysis of selected mouse mutant strains.
a Representative photos of embryos and coronal µCT sections through the heart summarizing the outcomes of the conditional knockout strategies. Black arrows highlight edema, red arrowheads ventricular septal defects in the heart. Edema is also evident in the µCT scans by the gap between the skin and the solid tissue layer. For Smg9 cKO-E, the green arrow highlights a fully closed and well-developed ventricular septum, in contrast to constitutive KOs. Smg9 cKO-T hearts are in general developmentally improved compared to the constitutive KO. The rendering of the embryo-placenta schematic is from Perez-Garcia, et al. Placentation defects are highly prevalent in embryonic lethal mouse mutants. Nature 555, 463-468 (2018). b Embryo crown-rump length measurements of all 5 genotypes per strain. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM of Atp11a: WT n = 23, HET n = 30, KO n = 7, cKO-E n = 8, c-KO-T n = 4; Smg9: WT n = 31, HET n = 44, KO n = 8, cKO-E n = 10, c-KO-T n = 6; Ssr2: WT n = 16, HET n = 21, KO n = 6, cKO-E n = 8, c-KO-T n = 5 embryos. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The letters indicate statistical comparisons, where identical letters between samples mean no difference, but discrepant letters indicate significant changes. c Assessment of heart phenotypes in cKO embryos of all genotypes, displaying the two most informative measurements—ventricular hole size and ventricular septal space as inverse measure of myocardial thinning. Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Holm–Šídák’s multiple comparisons test. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) are indicated by distinct letters, whereas same letters represent p > 0.05. Schematics of hearts are color-coded to display the degree of abnormality in the various genetic constellations. Measurements were taken from individual control (WT/HET) and KO (KO, cKO) embryos matched across litters for Atp11a (WT n = 12, HET n = 13, KO n = 10, cKO-E n = 7, c-KO-T n = 3), Smg9 (WT n = 17, HET n = 6, KO n = 9, cKO-E n = 7, c-KO-T n = 6), Ssr2 (WT n = 16, HET n = 19, KO n = 13, cKO-E n = 7, c-KO-T n = 5). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. All exact p-values are provided in Supplementary Data 1.