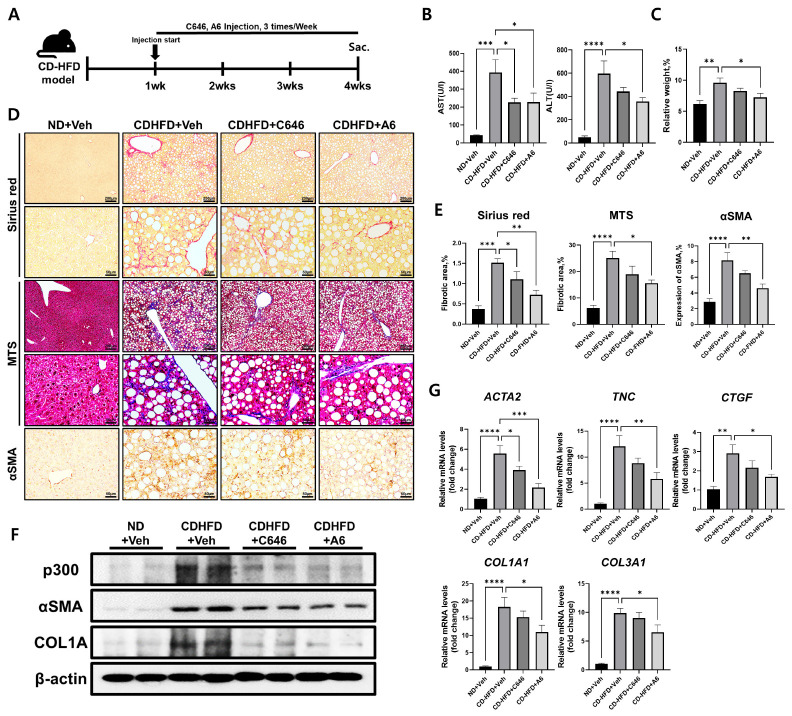
Fig. 2.
Amelioration of CD-HFD-induced liver fibrosis by p300 inhibitors. (A) Experimental design to investigate the effects of p300 inhibitors on CD-HFD-induced mouse liver fibrosis. Mice were fed CD-HFD for one week prior to treatment. Vehicle (0.01% DMSO 100 μl), C646 (5 mg/kg), or A6 (5 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally 3 times a week for an additional 3 weeks (n = 5). (B) Serum levels of AST and ALT after 4 weeks of CD-HFD, with or without p300 inhibitors (n = 5). (C) Average ratio of liver weight to body weight of mice on CD-HFD after treatment with vehicle, C646, or A6 (n = 5). (D, E) Representative photomicrographs (D) and percentages (E) of Sirius red staining, MTS, and IHC analysis of αSMA in mice liver tissues with or without p300 inhibitors at 4 weeks after CD-HFD (n = 5). (F) West-ern blot analysis of p300, αSMA, and COL1A in mice liver tissues with or without p300 inhibitors at 4 weeks after CD-HFD. β-actin was used as the sample loading control. (G) RT-qPCR expression analysis of fibrosis marker genes ACTA2 (αSMA), TNC, Col1a1, Col3a1, and CTGF in the mice liver with or with-out p300 inhibitors at 4 weeks after CD-HFD. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by ordinary one-way ANOVA test.