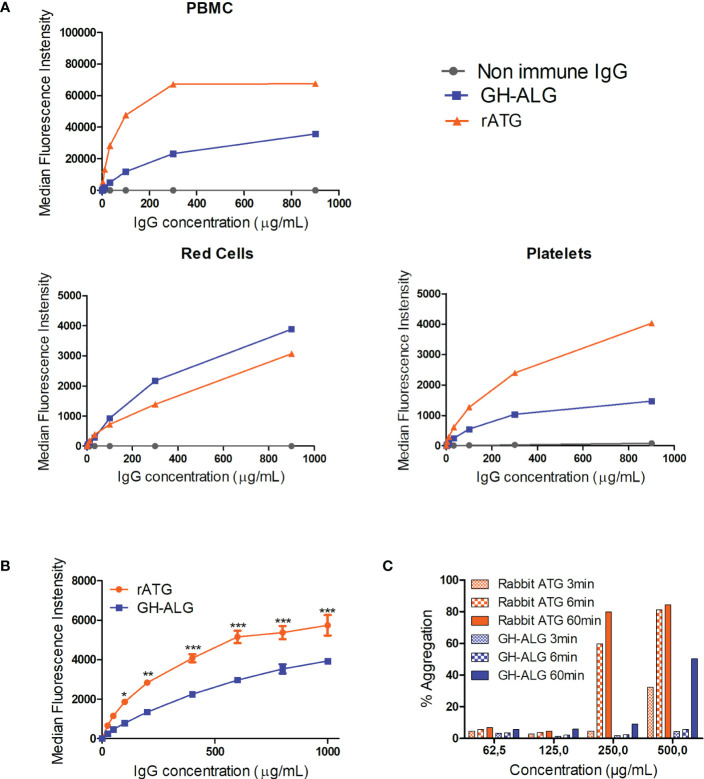
Figure 1.
Interaction between GH-ALG and human blood cells. (A) Binding of GH-ALG or rabbit ATG to human PBMCs, red cells and platelets was investigated by flow cytometry. Cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of GH-ALG or rabbit ATG. Nonimmune IgG was used as a control. After washing, bound IgG was detected by flow cytometry using a FITC-conjugated anti-pig antibody or FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody (N=3). (B) Direct comparison of GH-ALG and rabbit ATG binding to human platelets. Human platelets were incubated with increasing doses of GH-ALG or rabbit ATG. Attached antibodies were then detected using AF488-conjugated protein G and flow cytometry analysis. The data are expressed as means ± SEM (N=3). Two-way ANOVA (*, p<0.5; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.005). (C) Platelet aggregation assays. Human platelets were purified from citrated blood, and aggregation was measured by turbidimetry using a TA-8 V platelet aggregometer (Stago). One representative experiment from two is shown. .