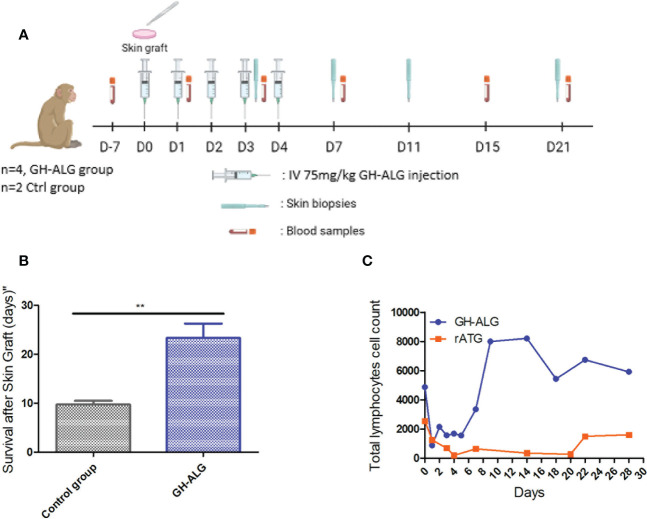
Figure 4.
In vivo efficacy of anti-lymphocyte IgG in NHP. (A) Timeline of the NHP skin graft study. (B) Skin grafts were performed on anesthetized animals on Day 0. After back skin shearing and asepsis, the animals were grafted in pairs (back skin collection using a 20 mm diameter template, followed by grafting and skin graft suturing). In the back of each animal, three grafts were performed: one autograft (as a control) and two pairwise allografts (one animal received skin transplants of his congener). Four cynomolgus monkeys intravenously received GH-ALG at 75 mg/kg once a day for 5 consecutive days. Four cynomolgus monkeys were used as controls and did not receive treatment. Skin graft rejection was considered when the area of the necrotized part covered the full graft, and the whole graft site hardened. (C) GH-ALG and rabbit ATG-induced T-cell depletion in macaques. Cynomolgus monkeys (n=9) received I.V. daily doses of 50 mg/kg of GH-ALG for 5 days. Cynomolgus monkeys (n=2) received I.V. daily doses of 5 mg/kg of rabbit ATG for 5 days. ** between 0.001 and 0.01.