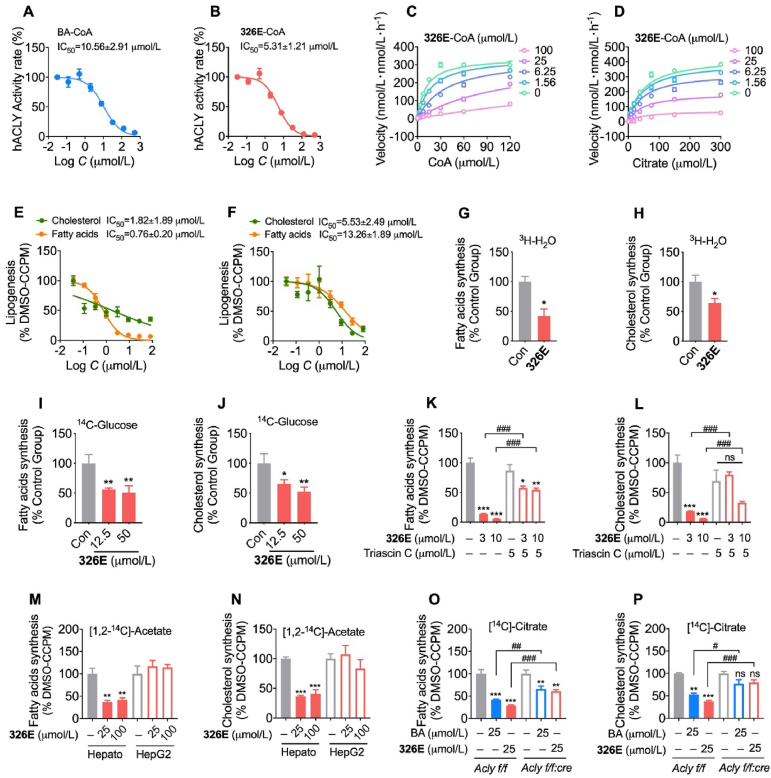
Figure 2.
326E inhibits ACLY activity and suppresses lipid synthesis in primary hepatocytes isolated from mice. (A)–(B) Dose-dependent inhibition of purified, recombinant ACLY after incubated with BA-CoA (A) and 326E-CoA (B), the activity at control was defined as 100%; (C)–(D) Recombinant human ACLY was incubated with indicated concentrations of 326E-CoA coenzyme A (C) or citrate (D). Ki was calculated by Michaelis-Menten kinetic analysis; (E)–(F) Hepatocytes from mouse were exposed to DMEM with control or multiple doses of 326E for 4 h in the presence of [1,2-14C]-acetate (E) or [14C]-citrate (F) as noted, and IC50 for de novo lipogenesis in the hepatocytes were generated; (G)–(J) Hepatocytes from mouse were exposed to DMEM with control or 326E for 4 h in the presence of [3C]-H2O or [14C]-glucose as noted, fatty acids (G, I) and cholesterol (H, J) biogenesis in the hepatocytes were showed; (K)–(L) ACSLs inhibitor triacsin C attenuates 326E induced lipogenesis in fatty acids (K) and cholesterol synthesis (L). Triacsin C (5 μmol/L) was pre-treated for 30 min before 326E treatment; (M)–(N) Hepatocytes isolated from mice or HepG2 cell lines were exposed to DMEM with control or 326E for 4 h in the presence of [1,2-14C]-acetate as noted, and the radioactive contents of 14C-fatty acids (M) and 14C-cholesterol (N) incorporated by [1,2-14C]-acetate were counted by liquid scintillation counter; (O)–(P) Hepatocytes isolated from Acly f/f mice or Acly f/f:cre mice were exposed to DMEM with control, 326E or BA for 4 h in the presence of 0.1 μCi/well [14C]-citrate as noted, and the radioactive contents of 14C-fatty acids (O) and 14C-cholesterol (P) incorporated by [14C]-citrate were counted by liquid scintillation counter. Data are mean ± SEM; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared toControl (Con). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 compared to indicated group. ns, not significant.