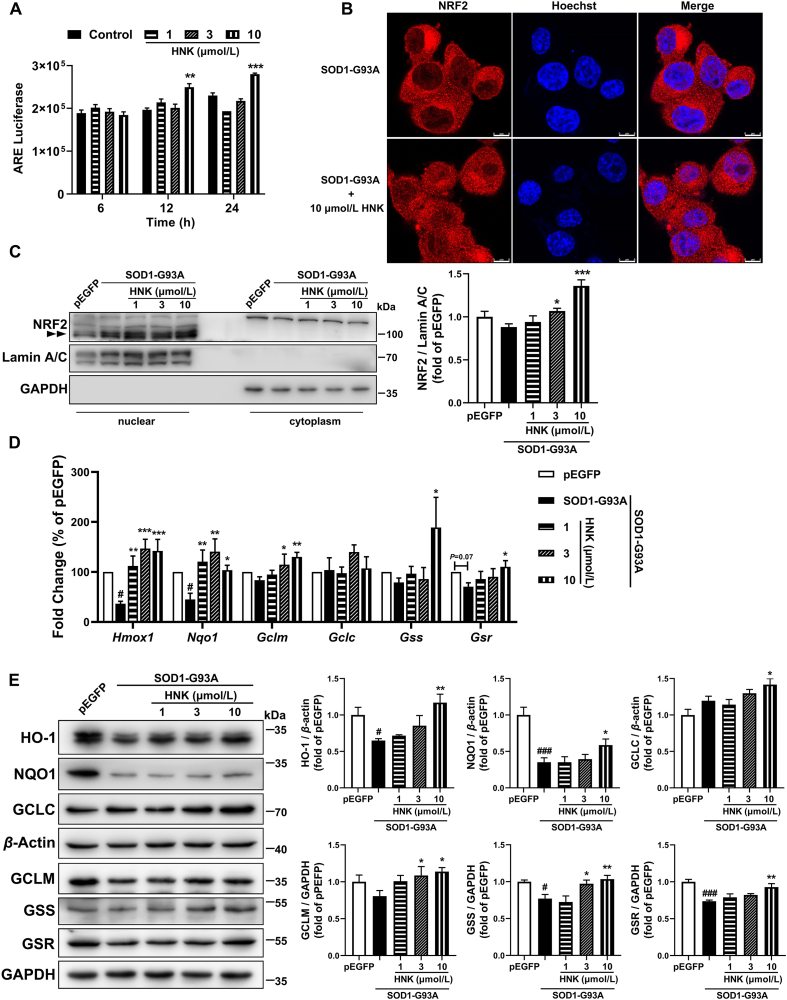
Figure 5.
Honokiol activated the NRF2 anti-oxidant pathway in the SOD1-G93A cells. (A) Luminescence intensity of HEK293-ARE reporter cells after treatment with indicated concentrations of honokiol for 6, 12 and 24 h (n = 3); (B) Representative images of NRF2 nuclear translocalization after 24 h honokiol treatment. Scale bars, 8 μm; (C) Western blot analysis and quantification of NRF2 in nuclear and cytoplasmic cell lysates after 24 h honokiol treatment (n = 4); (D) RT-qPCR analysis of transcription levels of Hmox1, Nqo1, Gclm, Gclc, Gss and Gsr after 12 h honokiol treatment (n = 3–7); (E) Western blot analysis and quantification of HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, GCLM, GSS and GSR in total cell lysates after 24 h honokiol treatment (n = 3–6). One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc LSD test was used for the comparison among three or more groups (SPSS 16.0). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 versus pEGFP control group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus SOD1-G93A model group.