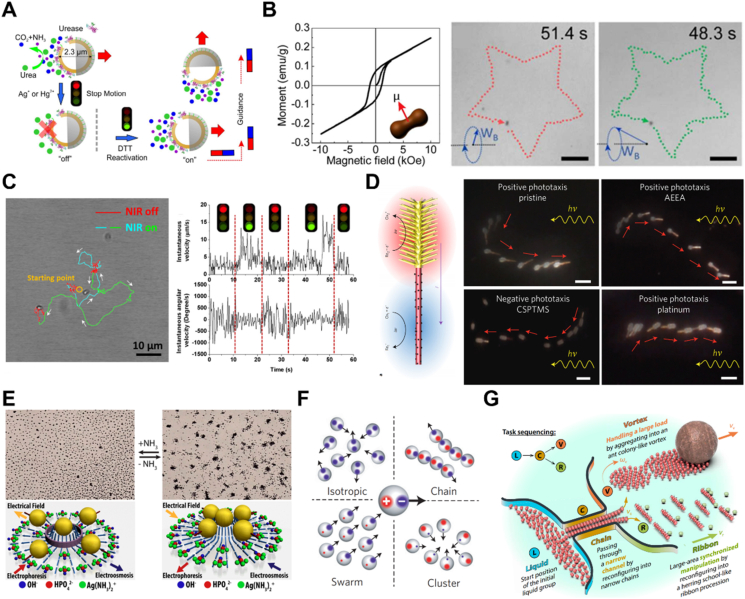
Figure 4.
Control on the motion direction and motion behavior of MNMs. (A) Motion control of enzyme-driven motor by chemical addition and magnetic fields. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 7. Copyright © 2016 American Chemical Society; (B) controlled motion pattern and trajectory of the peanut motor under magnetic field. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 124. Copyright © 2018 American Chemical Society; (C) motion behavior of CNB motor controlled by NIR light. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 121. Copyright © 2018 Wiley–VCH; (D) positive and negative phototaxis of artificial nanotree programmed by chemical modification. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 17. Copyright © 2016 Nature Publishing Group; (E) exclusion and schooling behaviors of Ag3PO4 microparticles by adding or removing NH3. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 132. Copyright © 2013 American Chemical Society; (F) formation of different collective states by the spheres with imbalanced, off-centered charges that triggered by an electric field. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 138. Copyright © 2016 Nature Publishing Group; (G) collective manipulation of micro-robotic swarms for completing the tasks. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 109. Copyright © 2019 American Association for the Advancement of Science.