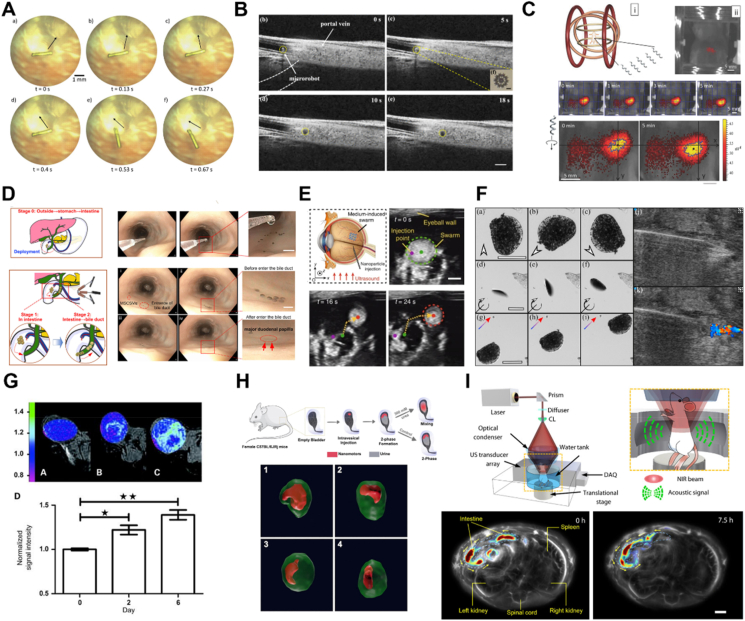
Figure 5.
In vivo navigation of MNMs. (A) Microrobot in lapine vitreous tracked by microscopy. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 142. Copyright © 2013 The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology; (B) tracking and navigation of magnetically-driven micromotors in a mouse portal vein by OCT. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 145. Copyright © 2019 IEEE; (C) navigation of a swarm of ABFs in the intraperitoneal cavity using FL imaging. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 146. Copyright © 2015 Wiley–VCH; (D) rapid delivery of MNMs to the bile duct via a natural orifice under the navigation of endoscopy. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 148. Copyright © 2021 American Association for the Advancement of Science; (E) USI for tracking of a swarm of MNMs in the bovine eyeball. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 134. Copyright © 2019 Nature Publishing Group; (F) the tracking of mobile hairbots under color Doppler imaging in a chicken breast ex vivo. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 150. Copyright © 2019 Elsevier; (G) biohybrid magnetotactic micromotors capable of colonizing mouse tumor xenografts and producing positive MRI contrast. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 151. Copyright © 2009 American Association for Cancer Research; (H) PET-CT analysis of 18F-nanomotors biodistribution in the bladder. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 8. Copyright © 2021 American Association for the Advancement of Science; (I) time-lapse PAI images of MNMs in intestines for 7.5 h. Reprinted with the permission from Ref. 54. Copyright © 2019 American Association for the Advancement of Science.