Fig. 3.
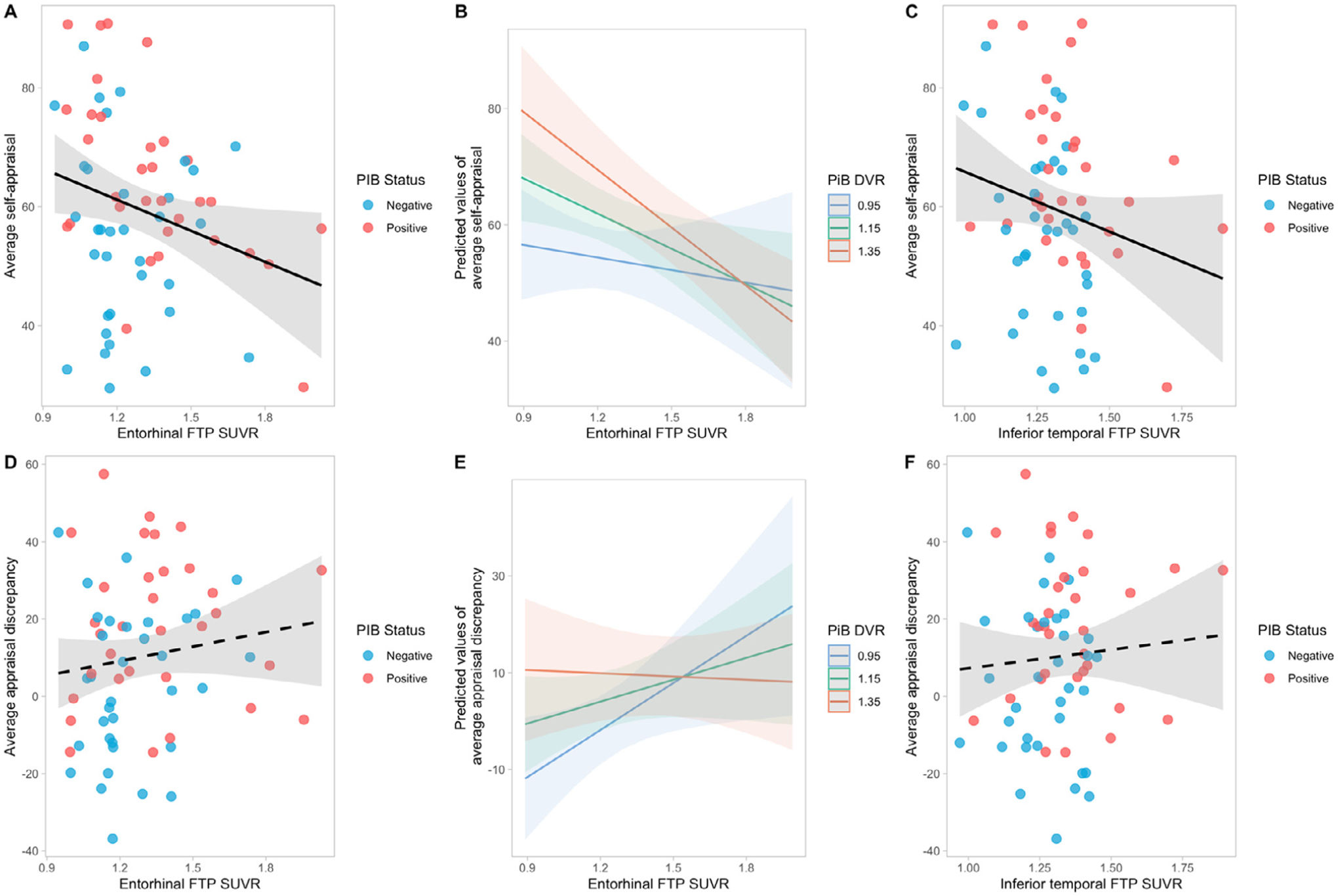
Relationship between self-appraisal/appraisal discrepancy and AD biomarkers, adjusting for age, sex, education, and GDS. Higher entorhinal FTP SUVR was significantly associated with lower average self-appraisal ratings (A), especially in individuals with higher global PiB DVR (B). Higher inferior temporal FTP SUVR was related to lower average self-appraisal ratings (C) but there was no significant interaction between global PiB DVR and inferior temporal FTP SUVR. (D) shows the relationship between entorhinal FTP SUVR and average appraisal discrepancy. There was a significant interaction between global PiB DVR and entorhinal FTP SUVR: higher entorhinal tau was related to greater average appraisal discrepancy (overestimation) but in individuals with lower amyloid level; this interaction is unlikely to be biologically significant (see text) (E). There was no significant association between inferior temporal FTP SUVR and average appraisal discrepancy (F). FTP. Flortaucipir; SUVR, standardized update value ratio; GDS, geriatrics depression scale; PiB, Pittsburg compound B; PiB positivity DVR threshold, 1.065.
