Figure 1.
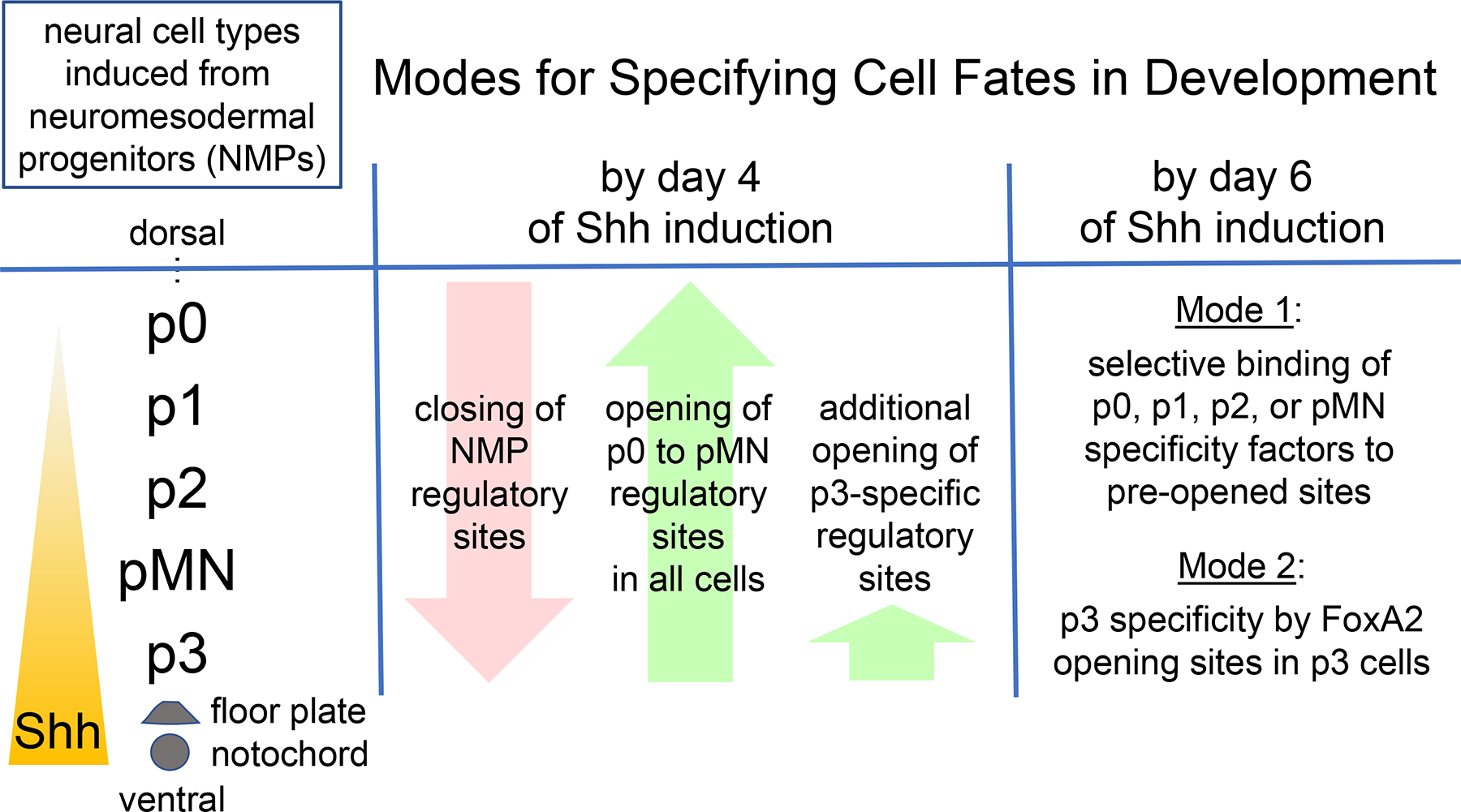
Two modes for cell fate induction in chromatin. Common neuromesodermal progenitors (NMPs) give rise to different neural tube fates, p0, p1, p2, pMN, and p3, in response to ventral Shh signaling from the notochord and the floor plate of the neural tube. In the embryonic stem cell-derived model of Melas et al. (2023), by four days of Shh induction, NMP regulatory sequences in chromatin become transposase-resistant, or “closed,” while regulatory sites for most of the neural fates become sensitive, or “opened.” By two days later, in Mode 1, different pre-open sites become targeted by newly induced factors that specify either the p0-p1, p2, or pMN fates. In Mode 2, additional regulatory sites become opened by FoxA2, which enables other factors to bind and activate the p3 neural fate.
