Fig. 3: VEGF-C-mediated retrograde transport and post-translational SUMOylation of NRP2B:
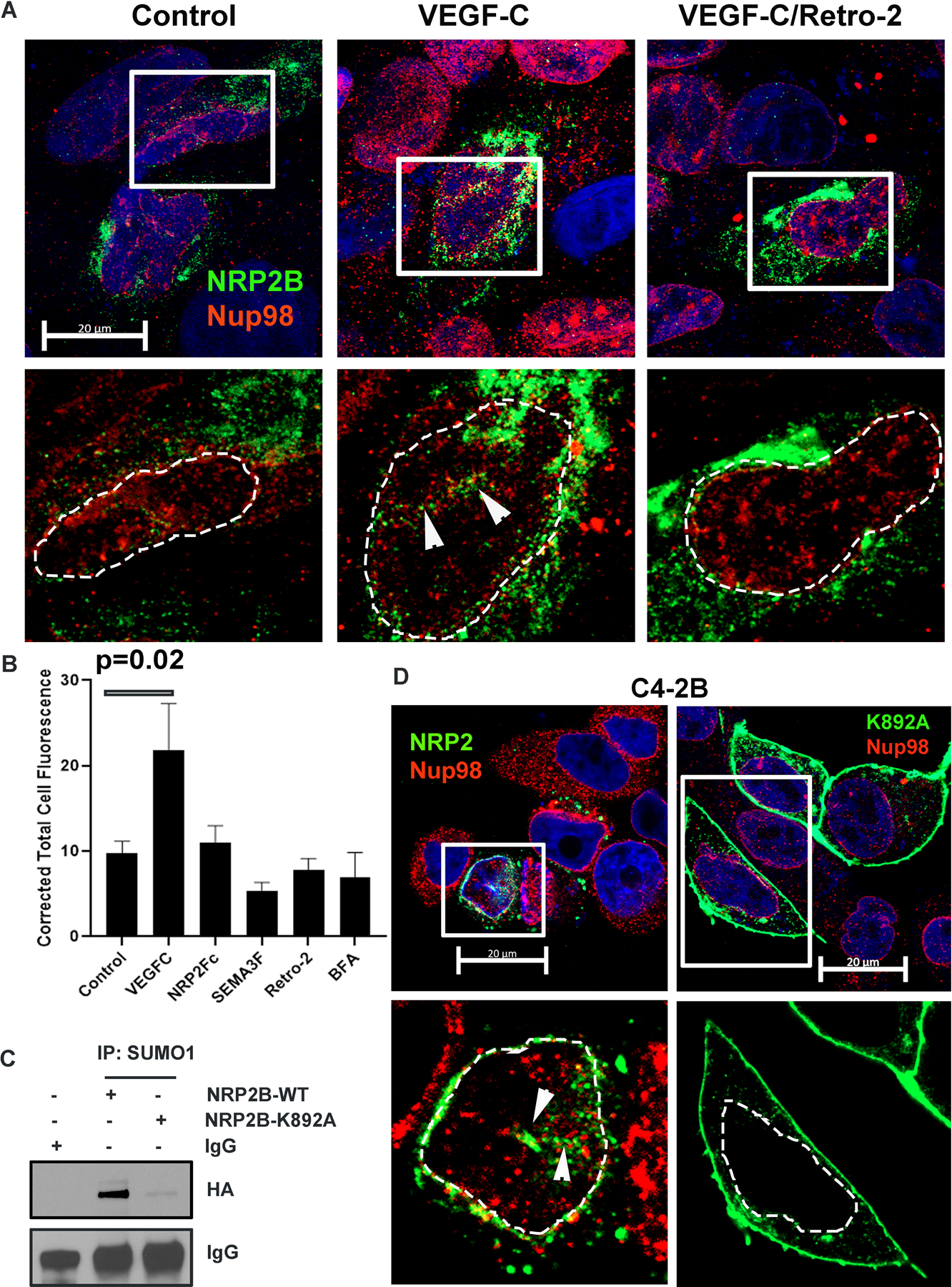
A. HA-tagged NRP2B was ectopically expressed in C4–2B cells. Immunofluorescence images representing the nuclear translocation of NRP2B under various conditions. NRP2B was detected using HA primary antibody and counterstained with Alexa 488-tagged secondary antibody. Arrowheads indicate invagination of the nuclear envelope. Nup98 was co-stained with NRP2. Inset is magnified. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. Nuclei are marked with dotted lines. Scale Bar 10 µm. B. Bar graph shows quantification of nuclear NRP2B. C. Immunoprecipitation with SUMO1 was carried out in C4–2B cells. HA-tagged wild type NRP2B and HA-tagged NRP2B K892A mutant were ectopically expressed in C4–2B cells. Immunoblots were carried out with HA-antibody. IgG bands show equal pulldown. D. Immunostaining of HA-tagged wild type and mutant K892A NRP2B in the C4–2B cell line. NRP2B was stained with HA-antibody and counterstained with secondary antibody labeled with Alexa 488. Nup98 was stained with Alexa 594. Arrowhead represents nuclear invagination in C4–2B cells expressing wild type NRP2B. Insets are magnified views. Nuclei are demarcated with dotted lines. DAPI indicates nucleus. Scale Bar 20 µm.
