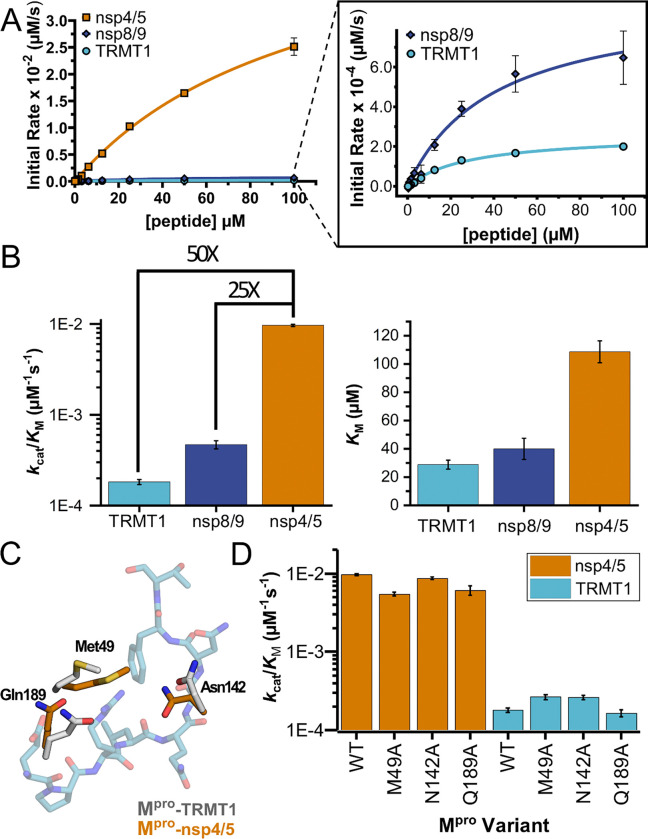
Figure 5. Human TRMT1 peptides are cleaved with similar catalytic efficiencies to known Mpro substrates.
A) Kinetics of nsp4/5, nsp8/9, and TRMT1 peptide cleavage by Mpro. To initiate the reaction, 50nM enzyme was added to 100–0.097 μM peptide. Each fluorogenic peptide was conjugated with a quenching moiety, and upon peptide cleavage, the fluorescence of the cleavage product was measured to determine initial rates of the reaction. Nsp4/5 cleavage rates were faster than those observed for the nsp8/9 or TRMT1 peptides, but nsp8/9 and TRMT1 sequences exhibit similar Mpro-mediated cleavage rates. B) The catalytic efficiency (kcat/KM) of TRMT1 peptide cleavage by Mpro is similar to that for nsp8/9 peptide cleavage; both of these substrates are cleaved significantly slower than the nsp4/5 sequence. This suggests that TRMT1 is a feasible substrate for Mpro. C) Illustration of changes in Mpro Met49, Asn142, and Gln189 residue positioning in TRMT1-bound (white) versus nsp4/5-bound (orange) structures. The TRMT1 peptide is shown in blue; nsp4/5 peptide is not shown. D) No major changes in catalytic efficiency are observed for nsp4/5 and TRMT1 peptide cleavage upon mutagenesis of key Mpro residues involved in TRMT1 binding and recognition. Primary fluorogenic kinetic data used to construct the plots and determine the kinetic parameters shown in A – D are listed in Dataset S1; numerical kcat, KM, and kcat/KM values are listed in Table S3.