Figure 4 -.
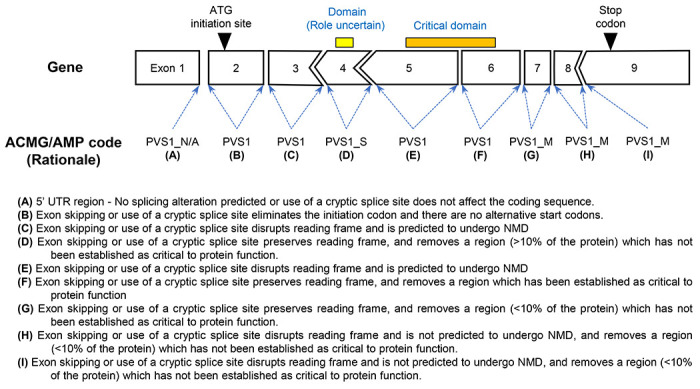
Decision tree for application of bioinformatic codes and RNA splicing assay results for variant interpretation. Footnotes: (a) Alternative prediction tools/thresholds may be appropriate for variants that impact sites other than GT-AT donor-acceptor motifs. (b) LP variants at the canonical positions should only be used as evidence if additional supporting clinical evidence is present. (c) Silent (excluding last 3nt of exon and first nt of exon) and intronic variants at or beyond the +7 and −21 positions (conservative designation for splice region) or otherwise as at or beyond the +7 and −4 positions (less conservative designation for minimal splice region). (d) If multiple impacts are observed from a splicing assay, use flowchart for the most conservative application of PVS1 based on experimental data. (e) We recommend that these thresholds be refined and applied in a disease- and gene-specific manner, including advice from Variant Curation Expert Panels. Categorization as complete or near complete needs to consider multiple factors, including assay/technique, RNA source, and validation of assay weights using established controls. Examples of laboratory-specific approaches and suggested operational thresholds have been reported previously.31; 58–61
