Fig. 1.
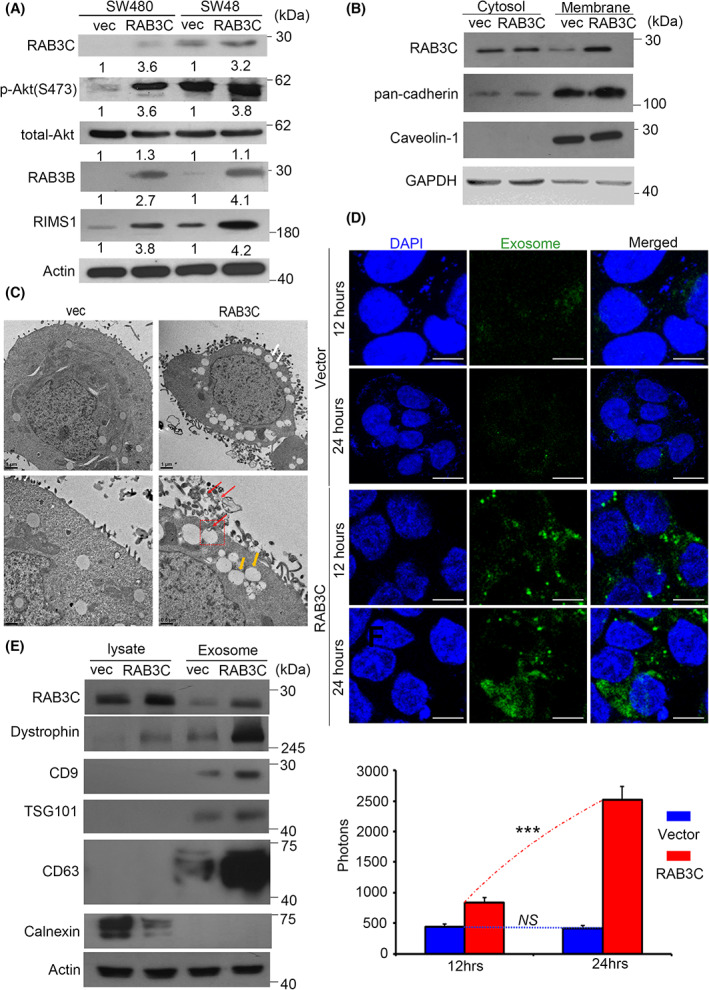
RAB3C regulates signaling transduction, vesicle formation, and exocytosis. (A) Western blots showing the RAB3C, total‐/phosphor‐Akt, RAB3B, and RIMS1 in the RAB3C‐overexpression models. (B) Intracellular expression of RAB3C in CRC cells after definition of cytoplasm/cell membrane. (C) Representative images of RAB3C‐expression model in SW480 cells examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). White arrows indicate exocy.tosis; yellow and red arrows indicate ILVs and MVBs, respectively. ILVs: intraluminal vesicles; MVBs: multivesicular bodies. Scale bar: 1 and 0.5 μm, respectively. Red arrows indicate exosomes. (D) (upper) Representative images and (lower) quantification of exosomes between vector and RAB3C‐overexpression models in SW480 cells examined by confocal microscopy. Analysis represents exosomal membranes. Blue: DAPI. Green: exosome membrane. Scale bar: 25 μm. (E) Western blot analysis of expressions of RAB3C, calnexin, dystrophin, CD9, CD63, and TSG101 of whole cells and exosomes isolated in RAB3C‐expression models. ***P < 0.001, NS, not significant. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Student's t‐test was used for the comparison of measurable variants of two groups. All experiments were performed with at least three biological duplicates (n = 3) for each group, in triplicate.
